Wildfires Intensify Global Forest Loss: A Record-Breaking Crisis
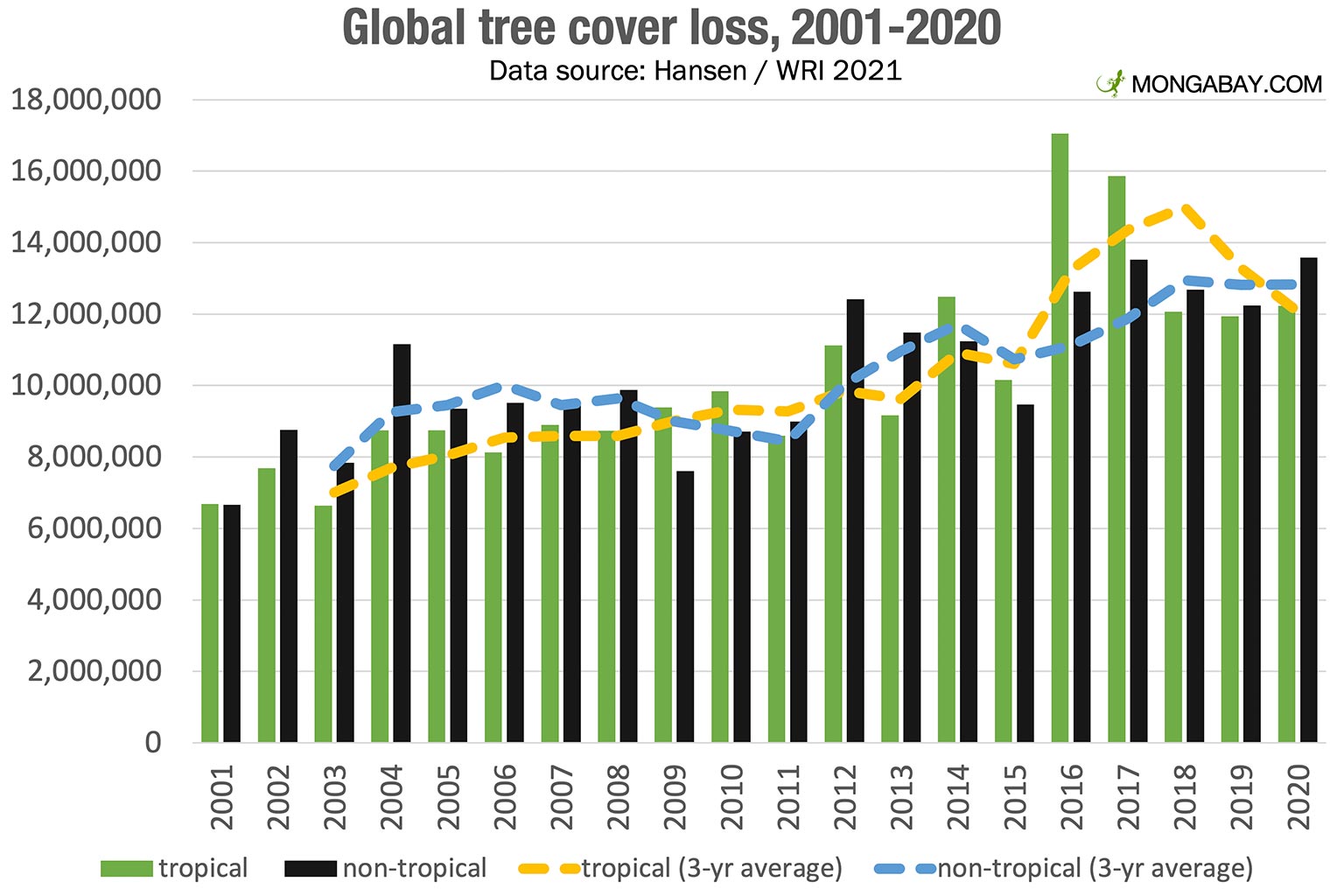
Table of Contents
The Growing Scale of Wildfires and Their Impact on Global Forest Loss
The frequency and severity of wildfires are dramatically increasing worldwide, resulting in catastrophic forest fire damage and unprecedented deforestation. This escalating trend poses a significant threat to global ecosystems and human well-being.
- Statistical Data: Reports from organizations like Global Forest Watch show a sharp rise in the area of forest burned annually. For example, [insert specific data and source - e.g., "Data from Global Forest Watch indicates a 40% increase in burned area between 2010 and 2020"]. These figures highlight the alarming increase in wildfire frequency and intensity.
- Devastating Examples: Major wildfires have ravaged vast areas of forest in recent years. The Amazon rainforest, Australia's bushfires, California's wildfires, and the Siberian fires are stark examples of the devastating impact on forest cover, leaving behind scarred landscapes and immense ecological damage. These events showcase the widespread nature of this global problem.
- Climate Change Correlation: The relationship between climate change and increased wildfire risk is undeniable. Higher global temperatures lead to drier conditions, longer fire seasons, and increased flammability of vegetation, creating a perfect storm for devastating wildfires. This positive feedback loop exacerbates the problem.
- Quantification of Forest Loss: The sheer volume of global forest loss due to wildfires is staggering. [Insert specific data and source – e.g., "Estimates suggest that wildfires accounted for X million hectares of forest loss in 2022 alone, a significant increase compared to the average of previous decades"].
- Economic Costs: The economic consequences of wildfires are also substantial, encompassing property loss, firefighting costs, damage to infrastructure, and the disruption of various industries like tourism and forestry. The costs associated with these events are enormous and continue to rise.
Underlying Causes Contributing to the Wildfire Crisis
The wildfire crisis is a complex issue with multiple contributing factors. Understanding these underlying causes is crucial to developing effective mitigation strategies.
- Climate Change's Role: Climate change is a primary driver, creating warmer, drier conditions that promote ignition and accelerate fire spread. Changes in weather patterns, including more frequent heatwaves and extreme droughts, increase the risk of intense and widespread wildfires.
- Deforestation and Land-Use Change: Deforestation and unsustainable land-use practices contribute significantly. The removal of trees reduces the landscape's moisture content, creating drier conditions that are more susceptible to fire. Poor forest management practices exacerbate the problem.
- Human Activity: Human activities, both accidental and intentional, are major ignition sources. Improperly discarded cigarettes, power lines, and deliberate arson are common causes of wildfires. Negligent actions greatly amplify the already existing risk.
- Invasive Species: The introduction of invasive plant species can alter forest ecosystems, increasing the fuel load and making them more prone to wildfires. These non-native species can outcompete native vegetation and create ideal conditions for fire.
- Drought Conditions: Prolonged drought significantly increases wildfire risk. Drier vegetation becomes highly flammable, providing ample fuel for fires to spread rapidly and intensely.
Environmental and Socioeconomic Consequences of Wildfires
The consequences of rampant wildfires extend far beyond the immediate destruction of forests. They have profound environmental and socioeconomic impacts on a global scale.
- Biodiversity Loss: Wildfires lead to massive habitat loss, driving species extinction and disrupting the delicate balance of ecosystems. The loss of biodiversity has cascading effects throughout the food chain.
- Air Pollution: Wildfires release massive amounts of smoke and pollutants into the atmosphere, causing significant air pollution and posing serious health risks. Respiratory illnesses, cardiovascular problems, and other health issues are common consequences.
- Climate Change Impact: Wildfires release enormous quantities of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, further exacerbating climate change and creating a dangerous feedback loop. This contributes to the very conditions that increase wildfire risk.
- Economic Impacts: The economic toll is substantial, including damage to property, infrastructure, and businesses. The disruption of livelihoods and loss of tourism revenue further add to the financial burden.
- Displacement and Humanitarian Crises: Wildfires frequently lead to the displacement of communities, creating humanitarian crises that require significant resources for relief and resettlement.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies to Combat Wildfires
Combating the wildfire crisis requires a multifaceted approach encompassing both mitigation and adaptation strategies. These efforts must be coordinated and implemented globally.
- Improved Forest Management: Sustainable forest management practices, including controlled burns (prescribed fires) to reduce fuel loads, are crucial. Reforestation efforts and selective logging can create more resilient forests.
- Enhanced Fire Prevention: Strengthening fire prevention measures involves public education campaigns to increase awareness of fire risks, stricter regulations on open fires, and improved infrastructure to prevent accidental ignitions.
- Early Warning Systems: Investment in advanced early warning systems and improved rapid response capabilities is essential for effective wildfire management.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions through the transition to renewable energy and other climate-friendly practices is vital to address the root cause of increased wildfire risk.
- Community Engagement: Engaging local communities in preparedness and response programs empowers them to protect their lives and property from wildfires.
- Technological Advancements: Utilizing technology, such as improved wildfire detection systems using satellites and drones, can enhance our ability to detect and respond to fires quickly.
Conclusion
The escalating frequency and intensity of wildfires are causing unprecedented global forest loss, with severe environmental and socioeconomic consequences. Climate change, deforestation, and human activity are key drivers of this crisis. Addressing this crisis demands immediate and concerted action on multiple fronts. We must invest in robust wildfire mitigation and adaptation strategies, strengthen forest management practices, and drastically reduce greenhouse gas emissions to combat climate change and protect our forests from further destruction due to devastating wildfires and global forest loss. Let's work together to prevent the devastating impact of wildfires and protect our planet's invaluable forests.

Featured Posts
-
 Gregor Robertsons Affordable Housing Plan Can We Increase Affordability Without A Market Crash
May 26, 2025
Gregor Robertsons Affordable Housing Plan Can We Increase Affordability Without A Market Crash
May 26, 2025 -
 Canli Mac Izle Atletico Madrid In Barcelona Karsilasmasi
May 26, 2025
Canli Mac Izle Atletico Madrid In Barcelona Karsilasmasi
May 26, 2025 -
 5 Must Try Shrimp Dishes In The Hudson Valley
May 26, 2025
5 Must Try Shrimp Dishes In The Hudson Valley
May 26, 2025 -
 Jadwal Siaran Langsung Moto Gp Inggris Sprint Race Di Trans7 Malam Ini Rins Vs Marquez
May 26, 2025
Jadwal Siaran Langsung Moto Gp Inggris Sprint Race Di Trans7 Malam Ini Rins Vs Marquez
May 26, 2025 -
 Nova Fotosesiya Naomi Kempbell Smilivi Ta Vidverti Obrazi
May 26, 2025
Nova Fotosesiya Naomi Kempbell Smilivi Ta Vidverti Obrazi
May 26, 2025
