Wildfires Threaten UK's Rarest Wildlife With Extinction
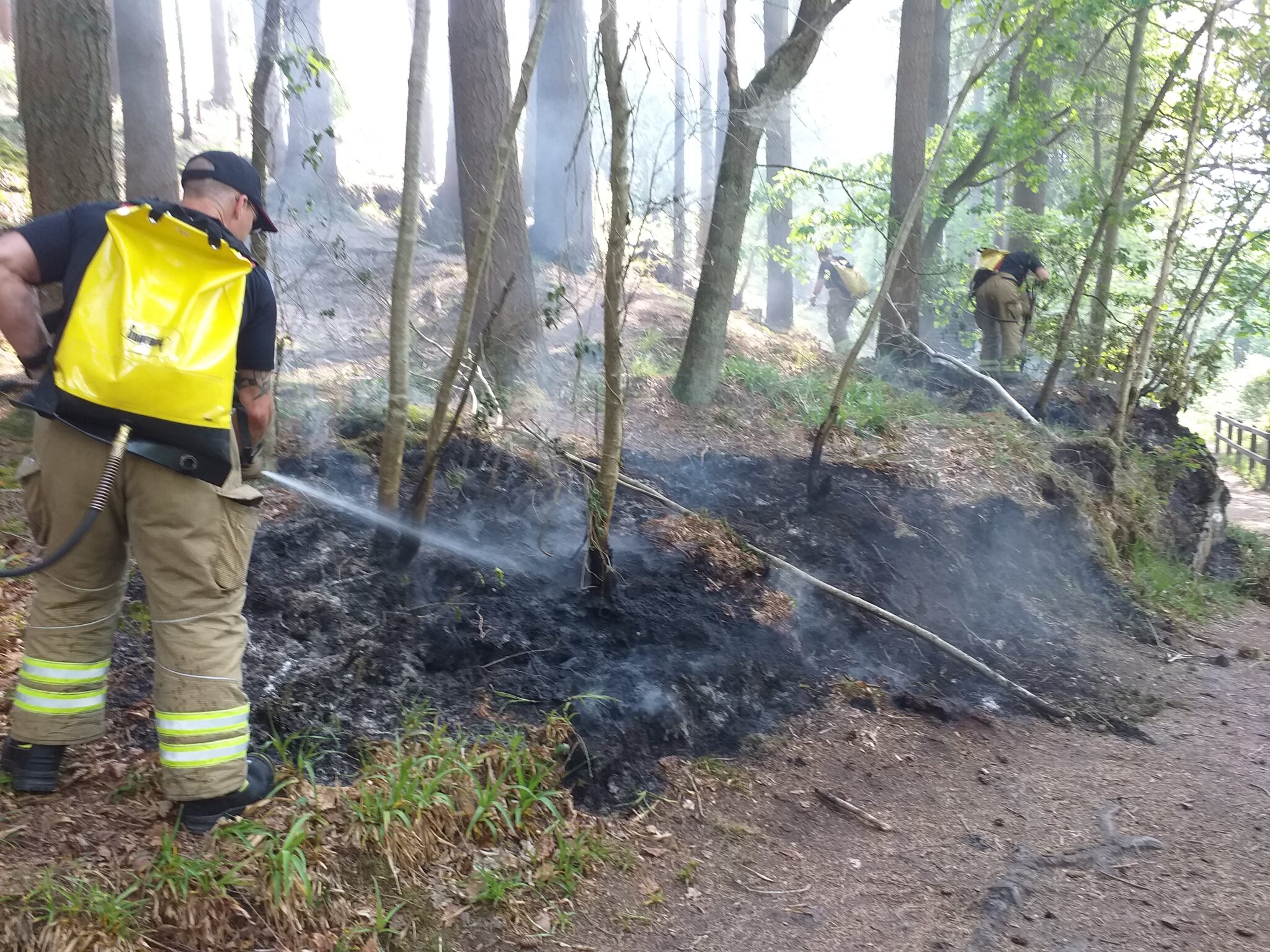

Table of Contents
The Devastating Impact of Wildfires on UK Habitats
Wildfires in the UK are causing widespread habitat destruction and ecosystem damage, leaving an indelible mark on the nation's landscapes. The impact is particularly severe on vulnerable ecosystems like heathlands, peat bogs, and ancient woodlands – habitats that are slow to recover and often support a unique array of specialist species. The speed and intensity of these fires are devastating:
- Rapid Devastation: Wildfires can consume vast areas of habitat within hours, leaving behind a barren wasteland. The intense heat destroys not only vegetation but also the crucial soil structure and organic matter essential for regeneration.
- Long-Term Consequences: Habitat loss resulting from wildfires has long-lasting consequences. Soil erosion becomes rampant, leading to further degradation and preventing the natural recolonization of plants and animals. The loss of these habitats can be irreversible, particularly for slow-growing species and fragile ecosystems.
- Unique Habitats, Unique Species: The UK boasts unique habitats shaped by millennia of natural processes and human interaction. These habitats, such as the rare lowland heath, support species found nowhere else, making their loss an irreplaceable tragedy for global biodiversity.
Endangered Species Facing Extinction Due to Wildfires
The devastating impact of UK wildfires extends directly to numerous endangered species, pushing them closer to the precipice of extinction. The loss of habitat directly translates to loss of life and a catastrophic disruption of delicate ecological balances.
- The Dartford Warbler: This rare bird, dependent on heathland for nesting and foraging, is highly vulnerable to wildfires which destroy its breeding habitat and food sources.
- The Smooth Newt: This amphibian relies on specific wetland habitats, easily destroyed by fire, for breeding and survival. Wildfires eliminate these crucial breeding grounds, drastically reducing populations.
- The Large Heath Butterfly: This butterfly is highly specialized to the specific microclimates found in heathland habitats. Wildfires destroy its larval food plants and the structure of its habitat, resulting in population crashes.
The loss of these and other species has knock-on effects throughout the food chain, destabilizing entire ecosystems and further diminishing the UK's already fragile biodiversity. Recent reports highlight the alarming extinction risk these species face due to increasingly frequent and severe wildfires.
Climate Change and the Increased Risk of Wildfires in the UK
The increasing frequency and intensity of wildfires in the UK are inextricably linked to climate change. Rising global temperatures, prolonged periods of drought, and more extreme weather events create ideal conditions for wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly.
- Rising Temperatures and Droughts: Data shows a clear correlation between rising temperatures and increased wildfire risk. Longer, hotter, and drier summers leave vegetation more susceptible to ignition and allow fires to burn more intensely.
- Human Activity: Human negligence, such as discarded cigarettes, unattended barbecues, and agricultural practices, also contribute significantly to wildfire ignition.
- Future Scenarios: If climate change continues unabated, we can expect a dramatic increase in the frequency, intensity, and geographic spread of wildfires in the UK, with devastating consequences for our environment and wildlife.
Conservation Efforts and Mitigation Strategies
Protecting the UK's biodiversity from the threat of wildfires requires a multi-pronged approach combining prevention, mitigation, and active conservation. Several organizations and initiatives are working to address this crisis:
- Controlled Burns: Prescribed burns, conducted under controlled conditions, can help reduce fuel loads and prevent more destructive wildfires.
- Improved Firebreaks: Creating and maintaining firebreaks – barriers that slow or stop the spread of wildfires – is a crucial aspect of wildfire management.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public about wildfire prevention and responsible land management is paramount.
- Habitat Restoration: Active restoration efforts are crucial to rebuilding damaged habitats after wildfires, aiding the recovery of endangered species.
Organizations like the RSPB, The Wildlife Trusts, and Natural England play vital roles in these conservation efforts. Community involvement and responsible land management practices are also crucial to minimizing the risk and impact of wildfires.
Conclusion
The threat of wildfires to the UK's rarest wildlife is undeniable and demands urgent action. The devastating impact on habitats, the risk of extinction for numerous species, and the clear link to climate change underscore the severity of the situation. Effective conservation strategies, including fire prevention measures, habitat restoration, and public awareness campaigns, are crucial to mitigating the damage and protecting our unique biodiversity. Protecting the UK's rarest wildlife from the threat of wildfires requires immediate and concerted action. Let's work together to safeguard our natural heritage.

Featured Posts
-
 Post Quantum Cryptography Market Expansion Driven By Algorithmic Advancements And Migration Timelines
May 13, 2025
Post Quantum Cryptography Market Expansion Driven By Algorithmic Advancements And Migration Timelines
May 13, 2025 -
 Nhl Draft Lottery Gets A Makeover Live Drawing New Format
May 13, 2025
Nhl Draft Lottery Gets A Makeover Live Drawing New Format
May 13, 2025 -
 Comprehensive Senior Activity Calendar Trips Events And More
May 13, 2025
Comprehensive Senior Activity Calendar Trips Events And More
May 13, 2025 -
 Sixers Nba Draft Lottery Odds How To Watch And What To Expect
May 13, 2025
Sixers Nba Draft Lottery Odds How To Watch And What To Expect
May 13, 2025 -
 Mark Consuelos On Kelly Ripas Live Absence Bored To Death
May 13, 2025
Mark Consuelos On Kelly Ripas Live Absence Bored To Death
May 13, 2025
