Will The Bank Of Canada Cut Rates Again? Impact Of Tariffs On Employment

Table of Contents
Current Economic Climate and the Bank of Canada's Mandate
The Bank of Canada's mandate is twofold: to maintain price stability and to foster full employment. Price stability is typically defined by keeping inflation within a target range, usually around 2%. Currently, inflation rates may deviate from this target, impacting the Bank’s decision-making process. Simultaneously, analyzing current employment numbers, including the unemployment rate and job growth, is crucial in assessing the overall economic health.
- Recent Economic Indicators: The latest data on GDP growth, consumer spending, and business investment provide vital insights into the overall economic momentum. A slowing GDP growth rate, coupled with weakening consumer confidence, could signal a need for stimulative measures, such as interest rate cuts.
- GDP Growth and Employment Correlation: Historically, strong GDP growth has usually correlated with job creation and a lower unemployment rate. A decline in GDP growth often precedes a rise in unemployment.
- Consumer Confidence and Spending Habits: Consumer spending constitutes a significant portion of Canada's GDP. Decreased consumer confidence, often driven by economic uncertainty, can lead to reduced spending, further impacting economic growth and employment.
The Impact of Tariffs on Canadian Employment
Tariffs, essentially taxes on imported goods, significantly impact Canadian employment. They affect import/export businesses directly by increasing the cost of imported goods or reducing the demand for Canadian exports. This ripple effect extends across related industries and supply chains, affecting various sectors.
- Specific Industries Affected: Industries heavily reliant on imports or exports, such as manufacturing (particularly automotive parts) and agriculture (certain food products), are particularly vulnerable to tariff-related disruptions.
- Job Losses or Gains Attributed to Tariffs: While some industries might experience job losses due to decreased competitiveness, others could see job gains if tariffs protect domestic production. Precisely quantifying this impact requires complex economic modeling.
- Potential Relocation of Businesses: Businesses may relocate production to avoid tariffs, leading to job losses in Canada and potential gains in other countries.
Tariff Impact on Inflation
Tariffs contribute to inflationary pressures by increasing the cost of imported goods. This impact is amplified if businesses pass the increased cost onto consumers, driving up prices for various products. The Bank of Canada must carefully balance the need to control inflation with the need to support employment.
- Examples of Goods Affected: Increased import prices on goods like steel, aluminum, and certain food products due to tariffs directly impact consumer prices.
- Pass-Through Effect on Consumer Prices: The extent to which tariffs translate into higher consumer prices depends on factors such as supply chain elasticity and market competition.
- Inflation Control vs. Employment: The Bank of Canada faces a difficult trade-off: higher interest rates can curb inflation but may stifle economic growth and increase unemployment; conversely, lower interest rates stimulate the economy but risk higher inflation.
Predicting Future Bank of Canada Actions
Predicting whether the Bank of Canada will implement further interest rate cuts requires careful analysis of current economic data and future forecasts. Several factors influence this decision.
- Probability Assessment of Further Rate Cuts: Economic forecasting models, considering inflation rates, employment figures, and global economic conditions, help assess the likelihood of further Bank of Canada interest rate cuts.
- Alternative Monetary Policy Tools: Besides interest rate cuts, the Bank of Canada could employ other monetary policy tools like quantitative easing (QE) to stimulate the economy.
- Political and Global Economic Factors: Political instability, global trade wars, and international economic slowdowns can all influence the Bank of Canada’s decision-making process.
Conclusion
The decision regarding further Bank of Canada interest rate cuts rests on a complex interplay of economic factors, with the impact of tariffs on employment being a significant consideration. The current economic climate presents challenges, requiring careful analysis of the intricate relationship between tariffs, inflation, and employment to anticipate future Bank of Canada actions. To make informed decisions, stay abreast of upcoming economic data releases and Bank of Canada announcements. For in-depth analysis on the implications of Bank of Canada interest rate cuts, continue following reputable financial news sources.

Featured Posts
-
 Lego Pokemon Fan Made Gen 3 Starter Builds
May 14, 2025
Lego Pokemon Fan Made Gen 3 Starter Builds
May 14, 2025 -
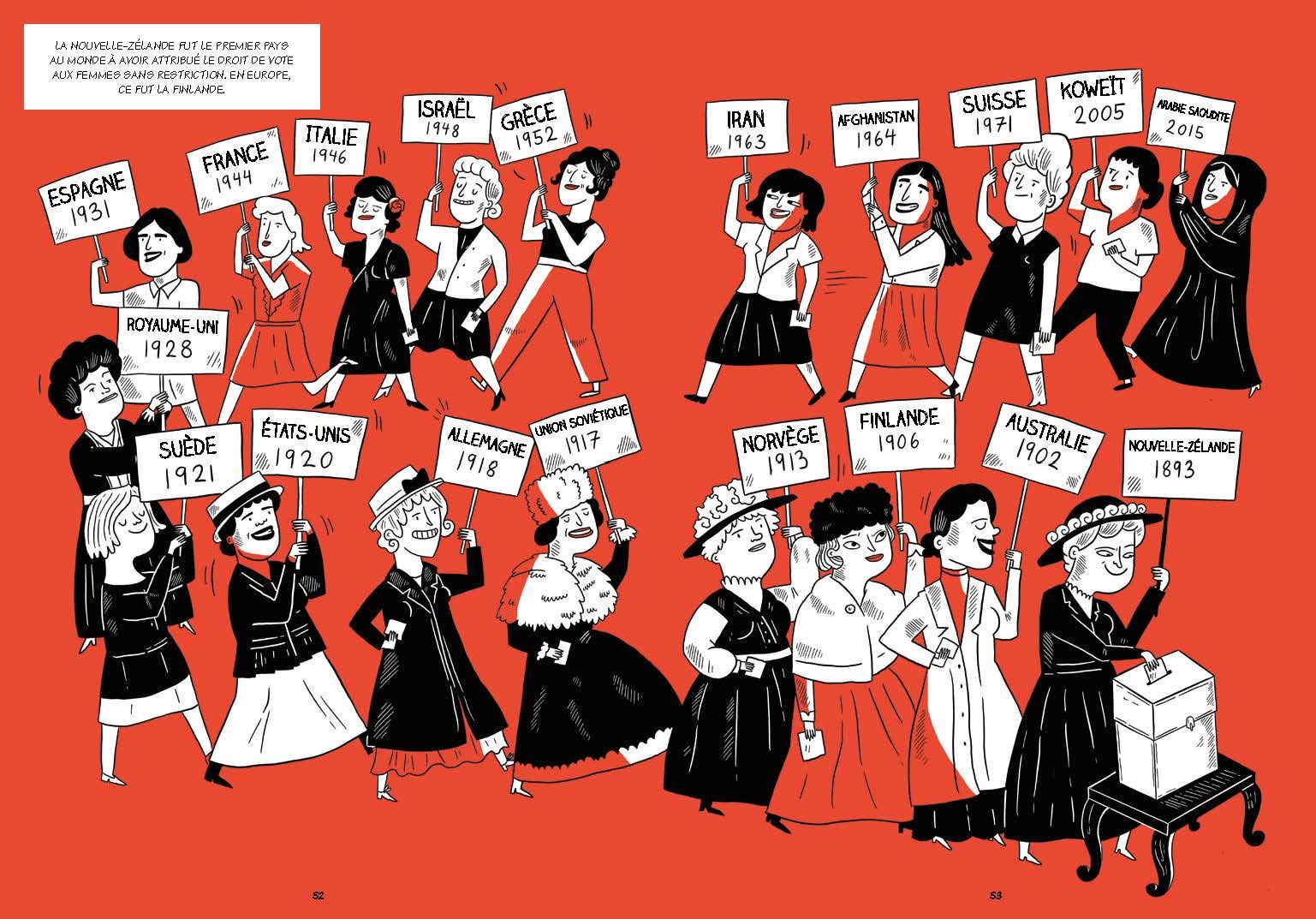 Droits De Vote Eramet Accedez Aux Informations Completes
May 14, 2025
Droits De Vote Eramet Accedez Aux Informations Completes
May 14, 2025 -
 The German Election A Final Opportunity For Change
May 14, 2025
The German Election A Final Opportunity For Change
May 14, 2025 -
 Super Eagles Striker Taiwo Awoniyi Undergoes Emergency Surgery
May 14, 2025
Super Eagles Striker Taiwo Awoniyi Undergoes Emergency Surgery
May 14, 2025 -
 Rachel Zegler At Snow White Spain Premiere Gal Gadots Absence Noted
May 14, 2025
Rachel Zegler At Snow White Spain Premiere Gal Gadots Absence Noted
May 14, 2025
