Analyzing The Great Decoupling: A Deep Dive Into Key Factors
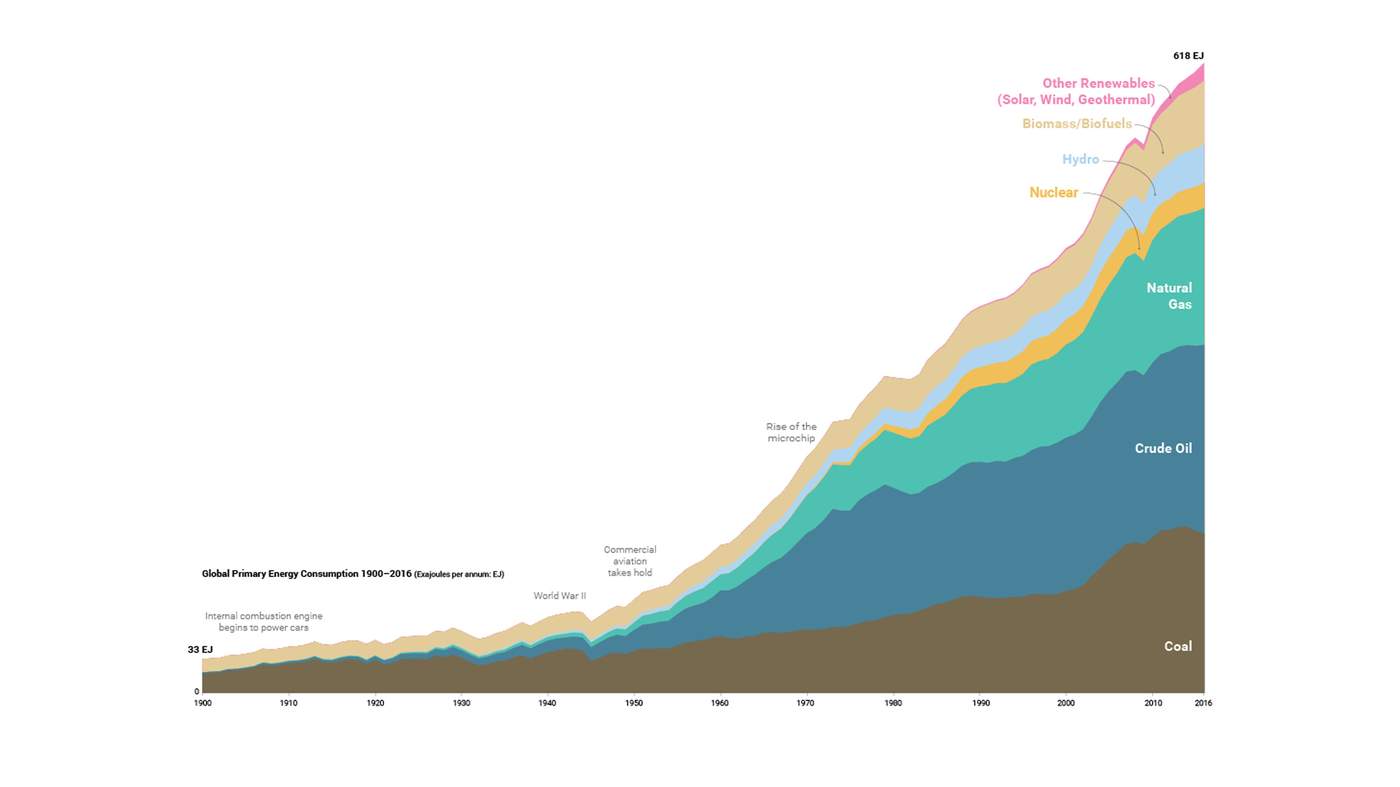
Table of Contents
Technological Advancements and Efficiency Gains
Technological innovation plays a pivotal role in achieving decoupling. Two key areas stand out: the renewable energy transition and improvements in energy efficiency across various sectors.
Renewable Energy Transition
The shift towards renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, is fundamental to "renewable energy decoupling." This transition reduces our reliance on fossil fuels, significantly lowering carbon intensity.
- Examples of successful renewable energy projects: The rapid growth of solar power in China, the expansion of offshore wind farms in Europe, and the increasing adoption of geothermal energy in Iceland demonstrate the potential for large-scale renewable energy deployment.
- Government policies supporting renewables: Many countries are implementing feed-in tariffs, renewable portfolio standards, and tax incentives to encourage renewable energy adoption. These policies are crucial drivers of "green energy transition."
- Technological breakthroughs in renewable energy storage: Advancements in battery technology and other energy storage solutions are addressing the intermittency of renewable sources, making them more reliable and efficient. This is vital for achieving consistent "carbon intensity reduction."
Energy Efficiency Improvements
"Energy efficiency decoupling" is achieved through the development and implementation of energy-efficient technologies across various sectors. This leads to more sustainable production and consumption patterns.
- Examples of energy-efficient technologies: LED lighting, energy-efficient appliances, smart grids, and improved building insulation are reducing energy consumption significantly.
- Policies promoting energy efficiency: Building codes, appliance efficiency standards, and energy efficiency labeling schemes incentivize the adoption of sustainable technologies.
- Impact of efficiency improvements on emissions: By reducing energy demand, energy efficiency improvements contribute directly to emission reduction strategies and overall "sustainable technologies" adoption.
Economic Structural Shifts and Consumption Patterns
Changes in economic structures and consumption patterns are also crucial for understanding the Great Decoupling. The shift in global value chains and changing consumer habits are particularly important.
Shifting Global Value Chains
Globalization and changes in manufacturing and production have a significant impact on carbon emissions. "Global value chain decoupling" can occur through responsible sourcing and manufacturing practices.
- Examples of relocation of industries: The shift of manufacturing from high-emission countries to those with stricter environmental regulations can lead to a decrease in overall emissions.
- Impact of automation on emissions: Automation can improve efficiency and reduce waste, potentially contributing to "carbon footprint reduction." However, the energy consumption of automation needs careful consideration.
- Role of international trade agreements: Trade agreements can either promote or hinder sustainable practices depending on their provisions related to environmental standards and regulations.
Changing Consumption Habits
Consumer behavior plays a significant role in resource use and emissions. "Sustainable consumption decoupling" relies on shifts towards more conscious purchasing decisions.
- Growth of the circular economy: The increasing adoption of reuse, repair, and recycling models reduces waste and resource consumption.
- Increasing demand for sustainable products: Consumers are increasingly demanding products made with sustainable materials and produced with low-emission processes.
- Impact of consumer awareness campaigns: Education and awareness campaigns promoting sustainable lifestyles are influential in changing consumer behavior and reducing their "consumer behavior and emissions."
Policy Interventions and Regulatory Frameworks
Government policies and regulations are crucial in driving the Great Decoupling. Effective carbon pricing and investments in green technologies are key components of this strategy.
Carbon Pricing Mechanisms
"Carbon pricing and decoupling" can be achieved through mechanisms like carbon taxes and emissions trading schemes.
- Examples of successful carbon pricing initiatives: The European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) and the carbon tax in Sweden have shown some success in reducing emissions.
- Challenges in implementing carbon pricing: Political resistance, concerns about competitiveness, and the need for effective revenue recycling are major challenges.
- Impact on emissions reduction: Well-designed carbon pricing mechanisms can significantly reduce emissions by incentivizing low-carbon alternatives.
Government Investments in Green Technologies
"Government policies and decoupling" are strongly influenced by public funding in green technology.
- Examples of government investments in green technology R&D: Many countries are investing heavily in research and development of renewable energy, energy storage, and other sustainable technologies.
- Subsidies for renewable energy: Government subsidies are crucial in making renewable energy sources competitive with fossil fuels.
- Impact of public funding on decoupling: Public funding plays a vital role in driving the innovation and deployment of "green technology investment" and fostering "public-private partnerships" which accelerate the transition to a sustainable economy.
Conclusion
Analyzing the Great Decoupling reveals a complex interplay between technological advancements, economic shifts, and policy interventions. Achieving sustainable decoupling requires a multifaceted approach addressing all these factors. Understanding these factors is critical for achieving sustainable development goals and mitigating climate change. We must continue to invest in renewable energy, promote energy efficiency, foster sustainable consumption patterns, and implement effective policies. We urge you to delve deeper into the issue of understanding the Great Decoupling through further research and engagement with organizations promoting sustainable practices. Let's work together to achieve sustainable decoupling and build a more sustainable future.

Featured Posts
-
 Nyt Strands Answers For Sunday February 23 2024 Game 357
May 09, 2025
Nyt Strands Answers For Sunday February 23 2024 Game 357
May 09, 2025 -
 Figma Vs Adobe Word Press And Canva How Ai Is Reshaping Design
May 09, 2025
Figma Vs Adobe Word Press And Canva How Ai Is Reshaping Design
May 09, 2025 -
 Tracking The Billions Musk Bezos And Zuckerbergs Post Trump Presidency Losses
May 09, 2025
Tracking The Billions Musk Bezos And Zuckerbergs Post Trump Presidency Losses
May 09, 2025 -
 Red Wings Fall To Golden Knights Hertls Impressive Performance
May 09, 2025
Red Wings Fall To Golden Knights Hertls Impressive Performance
May 09, 2025 -
 Investing In Palantir After A 30 Market Correction
May 09, 2025
Investing In Palantir After A 30 Market Correction
May 09, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 French Minister Advocates For Shared Nuclear Energy Security In Europe
May 09, 2025
French Minister Advocates For Shared Nuclear Energy Security In Europe
May 09, 2025 -
 Europes Nuclear Shield A French Ministers Perspective
May 09, 2025
Europes Nuclear Shield A French Ministers Perspective
May 09, 2025 -
 Mezhdunarodnaya Izolyatsiya Zelenskogo 9 Maya Bez Gostey
May 09, 2025
Mezhdunarodnaya Izolyatsiya Zelenskogo 9 Maya Bez Gostey
May 09, 2025 -
 Pakistan Economic Crisis Imf Reviews 1 3 Billion Aid Amidst Geopolitical Tensions
May 09, 2025
Pakistan Economic Crisis Imf Reviews 1 3 Billion Aid Amidst Geopolitical Tensions
May 09, 2025 -
 9 Maya Vladimir Zelenskiy Ostalsya Bez Podderzhki
May 09, 2025
9 Maya Vladimir Zelenskiy Ostalsya Bez Podderzhki
May 09, 2025
