Is Canada's Fiscal Policy Sustainable? Examining Liberal Economic Policies
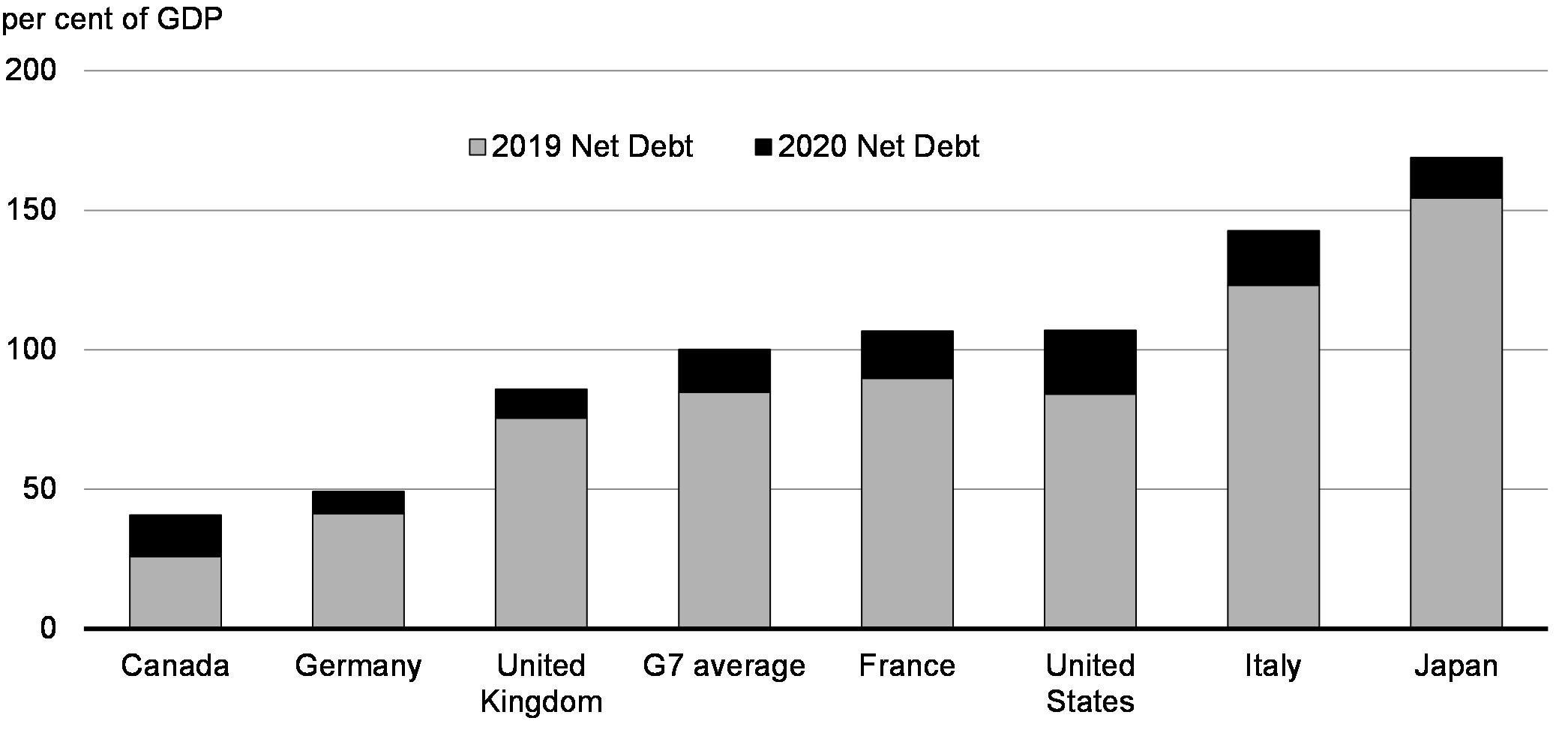
Table of Contents
Analyzing Canada's Debt-to-GDP Ratio: A Key Indicator of Fiscal Sustainability
The Current State of Canada's Debt
Canada's debt-to-GDP ratio, a crucial indicator of fiscal sustainability, has been steadily rising over the past decade. While precise figures fluctuate depending on the source and the specific year, it's clear that the ratio is significantly higher than it was a decade ago. Comparing Canada's ratio to other developed nations like the United States or those in the European Union reveals its position relative to global norms. This comparison helps contextualize the severity of the situation and understand the potential implications for future economic growth. A high debt-to-GDP ratio can limit a government's ability to respond effectively to economic crises or invest in crucial public services.
Factors Contributing to Rising Debt
Several factors have contributed to the increasing debt levels:
- Increased social program spending: Expanding social safety nets and increased demand for healthcare and social services due to an aging population place significant strain on government budgets.
- Infrastructure investments: While crucial for long-term economic growth, substantial investments in infrastructure projects, though beneficial, add to the national debt in the short term.
- Economic downturns and their impact on tax revenue: Recessions and economic slowdowns reduce tax revenue, widening the government's fiscal deficit and increasing the debt burden.
- Impact of global economic events: External shocks, such as global pandemics or trade wars, can significantly impact Canada's economy and government revenue, forcing increased borrowing.
Projected Debt Trajectory
Forecasts for Canada's future debt levels vary depending on the economic model used and the assumptions made about future economic growth and government spending. However, many projections suggest continued growth in the debt-to-GDP ratio unless significant policy adjustments are made. The potential risks associated with an unsustainable debt trajectory include higher interest payments, reduced government spending flexibility, and increased vulnerability to economic shocks. This underscores the importance of careful fiscal management and proactive policy adjustments.
Evaluation of Government Spending and Revenue Generation Strategies under Liberal Policies
Government Spending Priorities
Liberal economic policies have prioritized social programs, healthcare, and infrastructure investments. For example, the increase in funding for the Canada Child Benefit is a clear example of a significant social program expansion under Liberal leadership. While these investments are vital for social well-being and long-term economic growth, they significantly impact government spending, contributing to the rising debt. Analyzing the allocation of funds across various sectors allows for a comprehensive understanding of the government's spending priorities and their effect on the overall fiscal picture.
Taxation Policies and Revenue Generation
The effectiveness of Canada's taxation policies in generating sufficient revenue is crucial to fiscal sustainability. Current taxation policies, including personal and corporate income tax rates and indirect taxes like the Goods and Services Tax (GST), play a vital role in revenue generation. However, debates continue about potential tax reforms.
- Personal income tax rates and their effect on revenue: Adjusting personal income tax rates can impact both government revenue and individual disposable income, affecting consumer spending and economic growth.
- Corporate tax rates and their impact on investment: Corporate tax rates influence investment decisions by businesses and their overall contribution to the economy. Finding the right balance is essential to encourage investment and generate sufficient tax revenue.
- Effectiveness of indirect taxes (e.g., GST/HST): Indirect taxes represent a significant portion of government revenue. Examining their effectiveness and potential for reform is crucial for maintaining fiscal sustainability.
Impact of Economic Growth on Fiscal Sustainability
The relationship between economic growth and fiscal sustainability is complex. Strong economic growth generally leads to increased tax revenue, which can help reduce the debt-to-GDP ratio. However, fiscal policy plays a crucial role in stimulating economic growth. Government spending on infrastructure and social programs can boost economic activity, but it also contributes to the national debt. Finding the right balance between stimulating growth and controlling spending is essential for long-term fiscal health.
Potential Risks and Challenges to Canada's Long-Term Fiscal Sustainability
Demographic Changes and Aging Population
Canada's aging population presents a significant challenge to fiscal sustainability. As the proportion of elderly Canadians increases, so does the demand for healthcare services and social security benefits like pensions. These growing costs put immense pressure on government budgets, necessitating careful planning and potential policy adjustments to ensure the long-term viability of these crucial programs.
Global Economic Uncertainty
Global economic uncertainty poses a significant risk to Canada's fiscal sustainability. External shocks, such as trade wars, global recessions, or unexpected geopolitical events, can negatively impact Canada's economy, reducing tax revenues and potentially increasing government spending on social safety nets. Diversification of the economy and robust risk management strategies are crucial to mitigate these risks.
Climate Change and Environmental Costs
The costs associated with addressing climate change and mitigating its impacts present a growing fiscal challenge. Investments in renewable energy, climate adaptation measures, and environmental protection programs require significant financial resources. Failing to address these challenges adequately could lead to even greater economic costs in the future, emphasizing the need for proactive and long-term fiscal planning.
Conclusion: The Future of Canada's Fiscal Policy – A Path Towards Sustainability?
This examination of Canada's fiscal policy under Liberal governments reveals a complex picture. While investments in social programs and infrastructure are vital for the country's well-being, the rising debt-to-GDP ratio and the projected trajectory raise serious concerns about long-term sustainability. Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach that includes improving revenue generation strategies, enhancing the efficiency of government spending, and implementing long-term planning to address demographic challenges and the costs of climate change.
Further research and public discourse are crucial to ensuring Canada's fiscal policy remains sustainable for future generations. Join the conversation and help shape the future of Canada's economic landscape by researching the latest data on Canada's fiscal policy and advocating for policies that promote both economic growth and fiscal responsibility.

Featured Posts
-
 Pope Francis Legacy A More Global Yet Divided Church
Apr 24, 2025
Pope Francis Legacy A More Global Yet Divided Church
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Liams Collapse And Hopes New Living Arrangement The Bold And The Beautiful April 3 Recap
Apr 24, 2025
Liams Collapse And Hopes New Living Arrangement The Bold And The Beautiful April 3 Recap
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Canadian Auto Dealers Five Point Strategy To Navigate Us Trade Tensions
Apr 24, 2025
Canadian Auto Dealers Five Point Strategy To Navigate Us Trade Tensions
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Understanding The Crucial Role Of Middle Management In Todays Workplace
Apr 24, 2025
Understanding The Crucial Role Of Middle Management In Todays Workplace
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Lower Tesla Q1 Profits Examining The Political And Economic Context
Apr 24, 2025
Lower Tesla Q1 Profits Examining The Political And Economic Context
Apr 24, 2025
