Japan's Steep Bond Curve: A Deep Dive Into Investor Sentiment And Economic Outlook
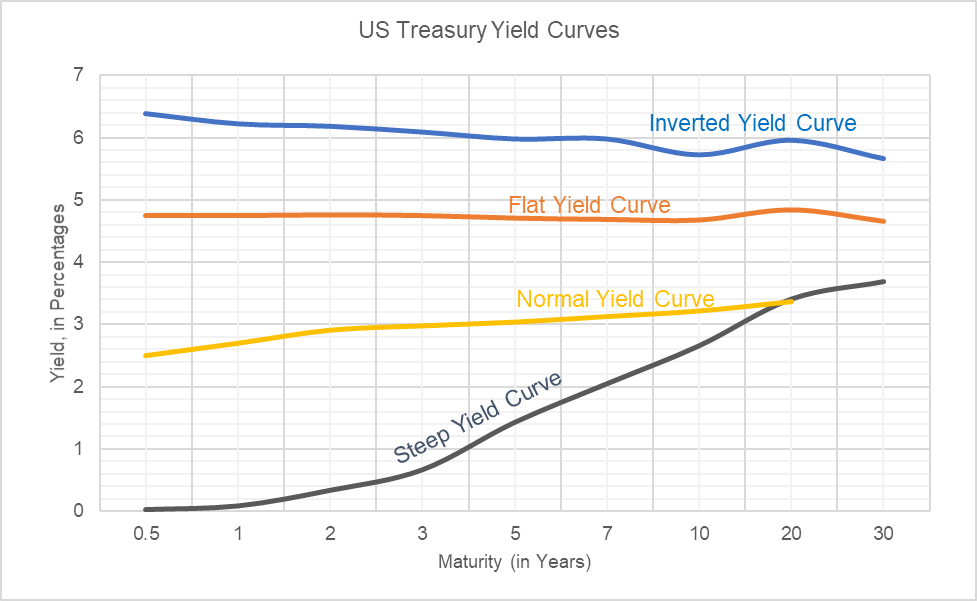
Table of Contents
The Mechanics of Japan's Steep Bond Curve
A steep yield curve represents a significant difference between short-term and long-term interest rates on government bonds. A steeper curve typically suggests expectations of future economic growth and higher inflation. Conversely, a flat or inverted curve often signals economic slowdown or recessionary concerns. Japan's current yield curve, specifically the Japanese Government Bond (JGB) yield curve, exhibits a pronounced steepness, a deviation from its historical norms and a key indicator of market sentiment.
-
Definition of yield curve and its various shapes (normal, inverted, flat): A yield curve plots the yields of bonds with different maturities. A normal yield curve slopes upward, indicating higher yields for longer-term bonds. An inverted yield curve slopes downward, while a flat yield curve shows little difference in yields across maturities.
-
Explanation of the current steepness of the Japanese government bond (JGB) yield curve: The recent steepening reflects a widening gap between short-term JGB yields (influenced by the Bank of Japan's monetary policy) and long-term yields (reflecting market expectations of future inflation and interest rates).
-
Comparison to historical yield curves in Japan: A comparison with historical JGB yield curves reveals a significant departure from the relatively flat curves observed in previous years, indicating a substantial shift in market expectations.
-
Visual aids (charts) showing the steepness: [Insert chart here visually depicting the steepness of the JGB yield curve, comparing it to historical data. Ensure chart is properly labeled and accessible.]
Underlying Factors Driving the Steep Curve
Several interconnected factors are driving the steepening of Japan's bond curve.
Inflationary Pressures
Japan is experiencing a rise in inflation, although it remains relatively moderate compared to other developed nations. This inflationary pressure, however, is impacting bond yields.
-
Impact of global inflation on Japan: Global inflationary pressures, driven by factors like supply chain disruptions and energy price increases, are transmitting to the Japanese economy, pushing up import prices and fueling domestic inflation.
-
Role of imported inflation: A significant portion of Japan's recent inflation is driven by imported goods, making the country vulnerable to global economic fluctuations and influencing JGB yields.
-
Analysis of the Bank of Japan's (BOJ) inflation targets: The BOJ's struggle to meet its inflation targets contributes to market uncertainty and affects investor confidence in the effectiveness of its monetary policies, thereby influencing the JGB yield curve.
BOJ Monetary Policy and its Limitations
The Bank of Japan's (BOJ) Yield Curve Control (YCC) policy aims to maintain low interest rates to stimulate economic growth. However, its effectiveness in managing the steepening yield curve is increasingly questioned.
-
Explanation of YCC and its aims: YCC involves the BOJ setting a target for the 10-year JGB yield and conducting bond purchases to maintain it.
-
Challenges faced by BOJ in managing inflation and yield curve: The BOJ faces a challenging balancing act: controlling inflation while maintaining low interest rates to support economic growth. The effectiveness of its current approach is under scrutiny.
-
Potential future changes to YCC: Speculation about potential changes or abandonment of YCC is creating market volatility and contributing to the steepening curve.
-
Market reaction to BOJ policy announcements: BOJ policy announcements are closely watched by investors, leading to significant market reactions and influencing the JGB yield curve.
Global Economic Uncertainty
Global economic uncertainty plays a significant role in shaping investor sentiment towards Japanese government bonds (JGBs).
-
Impact of US interest rate hikes on Japanese bond yields: The Federal Reserve's interest rate hikes attract global capital flows to the US dollar, putting downward pressure on the Japanese yen and impacting JGB yields.
-
Influence of global economic slowdown on investor risk appetite: Concerns about a potential global economic slowdown are causing investors to reassess risk and seek safe-haven assets, influencing the demand for JGBs.
-
Geopolitical risks and their impact on JGB demand: Geopolitical instability adds to uncertainty, potentially increasing the demand for JGBs as a safe-haven asset, counteracting the pressure from inflation.
Investor Sentiment and Market Behavior
The steepening yield curve has significantly impacted investor behavior.
-
Shifting investor preferences: Investors are adjusting their portfolios to reflect the changing landscape, moving towards shorter-term JGBs in anticipation of future interest rate hikes.
-
Increased demand for short-term JGBs: The demand for short-term JGBs is increasing due to their lower risk compared to longer-term bonds in a rising interest rate environment.
-
Impact on Japanese equity markets: The changes in bond yields are influencing investor sentiment towards Japanese equities, potentially impacting market valuations.
-
JPY exchange rate implications: The interplay between JGB yields and the Japanese Yen (JPY) exchange rate is significant, impacting both domestic and international investors.
Conclusion
The steepening of Japan's bond curve is a complex phenomenon resulting from rising inflation, limitations of the BOJ's monetary policy, and global economic uncertainty. Understanding investor sentiment and market behavior is crucial for navigating the Japanese market. The future trajectory of Japan's steep bond curve depends on the effectiveness of the BOJ's policy adjustments and the evolution of global economic conditions. Staying informed about the nuances of Japan's steep bond curve is essential for making informed investment decisions. Continue monitoring this key indicator to make strategic decisions in the Japanese financial market. Closely analyzing Japan's steep bond curve and its underlying drivers will be essential for success in the Japanese financial markets.

Featured Posts
-
 Trumps China Tariffs Projected To Stay At 30 Through 2025
May 17, 2025
Trumps China Tariffs Projected To Stay At 30 Through 2025
May 17, 2025 -
 Jackbit The Top Bitcoin Casino In The Usa
May 17, 2025
Jackbit The Top Bitcoin Casino In The Usa
May 17, 2025 -
 New York Knicks Star Player Seeks Reduced Court Time
May 17, 2025
New York Knicks Star Player Seeks Reduced Court Time
May 17, 2025 -
 Phoi Canh Cong Vien Dien Anh Thu Thiem De Xuat Moi Nhat
May 17, 2025
Phoi Canh Cong Vien Dien Anh Thu Thiem De Xuat Moi Nhat
May 17, 2025 -
 Jim Morrison Alive Fan Claims Hes A New York Maintenance Man
May 17, 2025
Jim Morrison Alive Fan Claims Hes A New York Maintenance Man
May 17, 2025
