National Average Gas Price Jumps By Almost 20 Cents
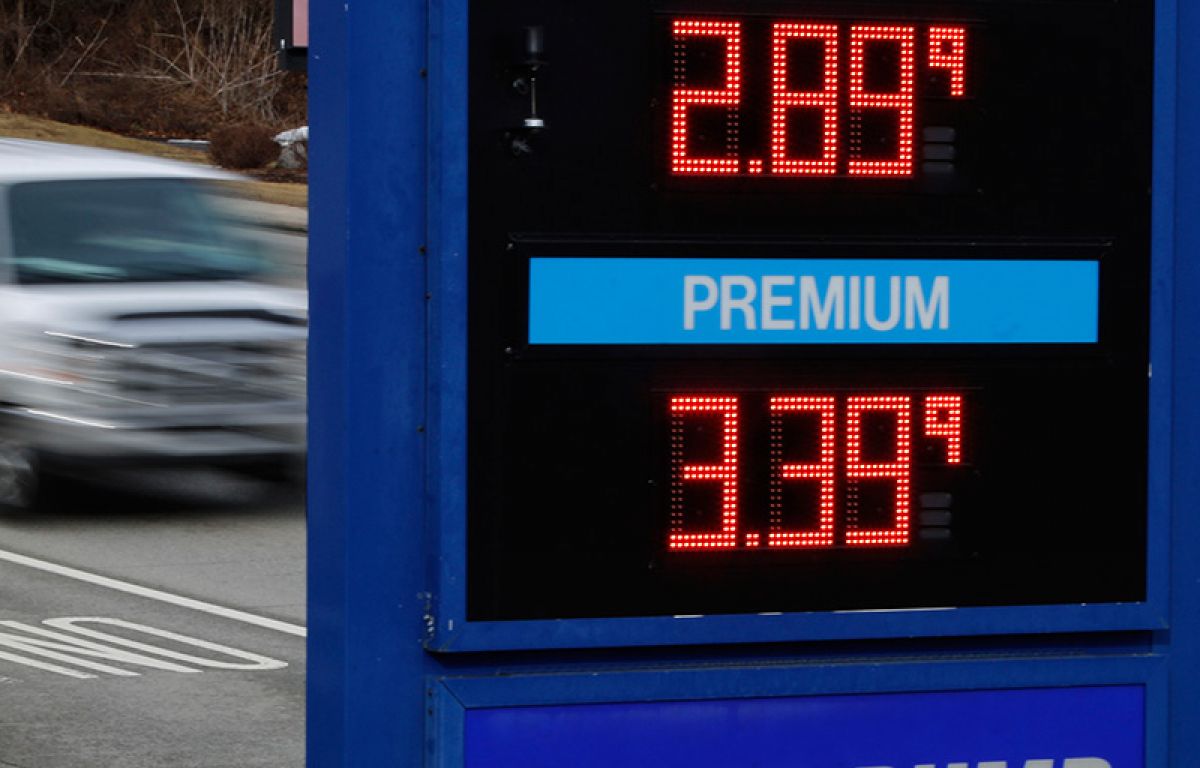
Table of Contents
Reasons Behind the Soaring Gas Prices
Several factors contribute to this dramatic increase in the national average gas price. Understanding these underlying causes is crucial to grasping the current situation and anticipating future trends.
Increased Crude Oil Prices
The price of crude oil, the primary ingredient in gasoline, is a major driver of fuel costs. Several global factors influence crude oil prices:
- Geopolitical Instability: Conflicts and political tensions in oil-producing regions create uncertainty and disrupt supply chains, leading to higher prices. The ongoing war in Ukraine, for example, has significantly impacted global oil supplies.
- OPEC Decisions: The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) plays a crucial role in regulating global oil production. Decisions regarding production quotas directly influence the availability and price of crude oil.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Global supply chain issues, exacerbated by the pandemic and other unforeseen events, continue to impact the efficient transport and delivery of crude oil, contributing to price volatility.
The relationship between crude oil and retail gas prices is direct: when crude oil prices rise, so do gas prices at the pump. A significant increase in crude oil prices almost always translates into a noticeable increase in the cost of gasoline for consumers.
Refinery Issues and Capacity
Operational issues at refineries can significantly impact gasoline supply. Reduced refining capacity due to:
- Planned Maintenance: Seasonal refinery maintenance schedules often lead to temporary production slowdowns, affecting gasoline supply.
- Unexpected Outages: Unforeseen events like equipment failures or natural disasters can cause significant refinery shutdowns, further restricting gasoline production.
These issues, combined with increased demand, create a supply shortage, driving up prices. Data on refinery capacity utilization rates can provide insights into the extent of these constraints and their impact on the national average gas price.
Seasonal Demand
Demand for gasoline typically increases during peak travel seasons, such as summer vacations and holidays. This surge in demand, coupled with potentially limited supply due to refinery issues, contributes to higher prices.
- Summer Travel: The summer months typically see the highest demand for gasoline due to increased road trips and leisure travel.
- Holiday Travel: Similar surges in demand occur during major holidays like Thanksgiving and Christmas.
Comparing current gas prices to those during similar periods in previous years highlights the extent of the current price increase and the role seasonal demand plays in price fluctuations.
Impact on Consumers and the Economy
The almost 20-cent jump in the national average gas price has far-reaching consequences for consumers and the overall economy.
Increased Transportation Costs
Higher gas prices directly translate into increased transportation costs for everyday consumers.
- Commuting: Daily commutes become more expensive, impacting household budgets.
- Shopping: Increased fuel costs make shopping trips more costly, potentially leading to reduced consumer spending.
- Travel: The cost of vacations and other travel plans rises, impacting leisure activities and potentially reducing travel frequency.
Budgeting strategies, such as consolidating errands, carpooling, or exploring alternative transportation options, are becoming increasingly vital for many households.
Inflationary Pressure
Rising gas prices contribute significantly to overall inflation. Increased fuel costs affect not only transportation but also the cost of goods and services across the economy.
- Transportation of Goods: Higher fuel costs for trucking and delivery services increase the price of goods, impacting consumers at the retail level.
- Manufacturing and Production: Businesses incur increased transportation costs for raw materials and finished products, adding to inflationary pressure.
Economic reports often demonstrate a strong correlation between fuel prices and inflation rates, highlighting the significant inflationary impact of rising gas prices.
Impact on Businesses
Businesses, particularly those relying heavily on transportation, face significant challenges due to increased fuel costs.
- Trucking and Delivery Services: These industries often experience substantial increases in operating costs, leading to potential price hikes for consumers or reduced profit margins.
- Retail Businesses: Increased transportation costs for inventory impact businesses' profit margins and might lead to price increases for consumers.
What Can Consumers Do?
While we can't control global factors influencing gas prices, we can take steps to mitigate their impact on our budgets.
Fuel Efficiency Tips
Improving fuel efficiency can significantly reduce gasoline consumption and costs.
- Regular Vehicle Maintenance: Ensure your vehicle is properly maintained, including regular tire inflation and oil changes.
- Efficient Driving Habits: Avoid aggressive acceleration and braking, and maintain a consistent speed.
- Reduce Weight: Removing unnecessary weight from your vehicle can improve fuel economy.
Comparison Shopping for Gas
Take advantage of resources that allow you to compare prices at different gas stations.
- Gas Price Tracking Apps: Several apps provide real-time gas price updates in your area.
- Websites: Many websites offer gas price comparison tools.
Alternative Transportation
Consider alternative transportation methods to reduce reliance on personal vehicles.
- Public Transportation: Utilize buses, trains, or subways when feasible.
- Carpooling: Share rides with colleagues or friends to reduce individual fuel consumption.
- Cycling: Cycling is a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative for shorter distances.
Conclusion
The almost 20-cent jump in the national average gas price is a result of a complex interplay of global events and economic factors, including increased crude oil prices, refinery issues, and seasonal demand. This surge has a significant impact on consumers, businesses, and the overall economy, contributing to increased transportation costs and inflationary pressures. To navigate these challenges, consumers should actively monitor gas prices, adopt fuel-saving strategies, and consider alternative transportation options. By understanding the dynamics of rising gas prices and taking proactive steps, you can better manage your budget and mitigate the impact on your finances. Remember to track gas prices regularly using available resources and make informed decisions to lessen the financial burden of these fluctuating fuel costs.
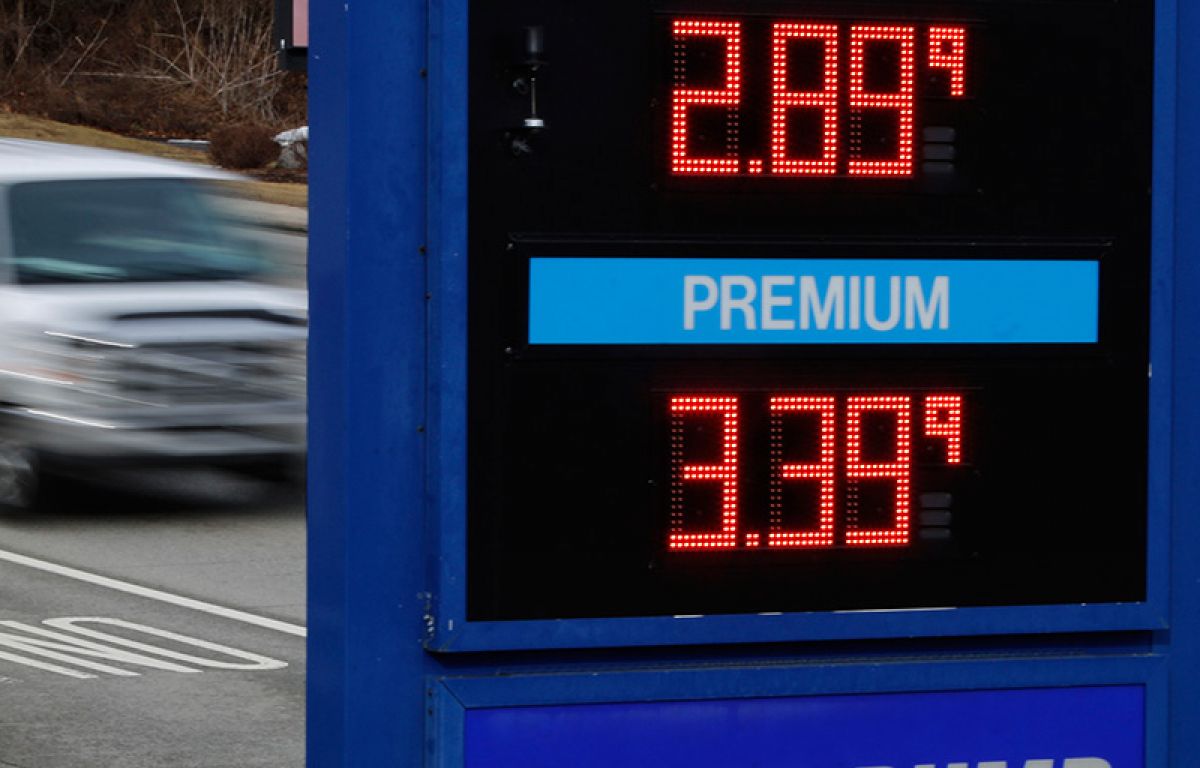
Featured Posts
-
 Significant Gas Price Hike Up Almost 20 Cents Per Gallon
May 22, 2025
Significant Gas Price Hike Up Almost 20 Cents Per Gallon
May 22, 2025 -
 Nuffy Touring With Vybz Kartel A Dream Realized
May 22, 2025
Nuffy Touring With Vybz Kartel A Dream Realized
May 22, 2025 -
 Kamerbrief Certificaten Abn Amro Programma Details En Strategieen
May 22, 2025
Kamerbrief Certificaten Abn Amro Programma Details En Strategieen
May 22, 2025 -
 Investment Insights Core Weave Inc Crwv And Its Recent Stock Gains
May 22, 2025
Investment Insights Core Weave Inc Crwv And Its Recent Stock Gains
May 22, 2025 -
 Bp Ceo Pay Cut A 31 Decrease In Executive Compensation
May 22, 2025
Bp Ceo Pay Cut A 31 Decrease In Executive Compensation
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The Karate Kid A Complete Guide To The Franchise
May 23, 2025
The Karate Kid A Complete Guide To The Franchise
May 23, 2025 -
 The Karate Kid A Look At Its Influence On Martial Arts And Popular Culture
May 23, 2025
The Karate Kid A Look At Its Influence On Martial Arts And Popular Culture
May 23, 2025 -
 Analyzing The Karate Kid Films Themes Characters And Storytelling
May 23, 2025
Analyzing The Karate Kid Films Themes Characters And Storytelling
May 23, 2025 -
 The Karate Kids Enduring Legacy Impact And Cultural Significance
May 23, 2025
The Karate Kids Enduring Legacy Impact And Cultural Significance
May 23, 2025 -
 The Karate Kid Exploring Mr Miyagis Wisdom And Training Methods
May 23, 2025
The Karate Kid Exploring Mr Miyagis Wisdom And Training Methods
May 23, 2025
