Posthaste: High Down Payments And The Canadian Housing Crisis

Table of Contents
The Impact of High Down Payments on Affordability
The escalating cost of homes in Canada necessitates larger down payments, often exceeding the traditional 20% of the purchase price. This requirement creates a significant barrier to entry for first-time homebuyers, particularly those with lower incomes or limited savings. The longer it takes to save for a substantial down payment, the more likely individuals are to be priced out of the market entirely, as home prices continue to climb. This creates a vicious cycle, where the dream of homeownership becomes increasingly unattainable for many.
- The Savings Gap: Saving for a 20% down payment on a home in major Canadian cities like Toronto or Vancouver requires years of diligent saving, often exceeding the average person's capacity.
- Income Inequality: High down payments exacerbate income inequality, disproportionately affecting lower and middle-class families who struggle to accumulate the necessary savings. This contributes to a widening gap between the haves and have-nots in the housing market.
- Geographic Disparity: The challenge of affording a down payment is particularly acute in major urban centers where home prices are significantly higher than in other parts of the country. This creates a geographic disparity in homeownership rates.
For example, according to the Canadian Real Estate Association (CREA), the average price of a home in Toronto in [Insert Current Year] was [Insert Data - cite source]. To afford a 20% down payment, a buyer would need [Calculate and insert amount], significantly exceeding the average income for many families in the city. This highlights the critical role down payments play in restricting access to homeownership.
The Role of Mortgage Rates in Amplifying the Problem
High interest rates significantly amplify the challenges posed by high down payments. Increased borrowing costs make it harder to qualify for a mortgage, even with a substantial down payment. Lenders, facing increased risk in a high-interest-rate environment, often demand larger down payments to mitigate potential losses. This creates a perfect storm: high home prices coupled with high-interest rates and high down payment requirements, making homeownership increasingly difficult to achieve.
- Interest Rate Hikes: Recent interest rate hikes by the Bank of Canada have further tightened lending conditions, making mortgages more expensive and reducing affordability.
- Increased Debt Burden: Higher mortgage rates lead to increased debt levels, potentially compromising the financial stability of homeowners. This can create a vulnerable position for borrowers facing unexpected financial challenges.
- Reduced Purchasing Power: The combined effect of high home prices, high interest rates, and large down payments significantly reduces the purchasing power of potential homebuyers.
The impact of the Bank of Canada's recent interest rate increases is evident in the decreased number of mortgage approvals and a slowing real estate market. This directly reflects the difficulties faced by potential buyers navigating the current conditions in the Canadian housing market.
Government Policies and Their Impact on Down Payments
Current government programs designed to assist first-time homebuyers, while helpful to some, often fall short in addressing the core issue of high down payments. Mortgage loan insurance, while mitigating some risk for lenders, does not significantly reduce the substantial upfront cost burden for buyers.
- First-Time Home Buyer Incentive: While the First-Time Home Buyer Incentive offers shared equity, its impact on overall affordability remains limited.
- Tax Policies: Current tax policies regarding homeownership and savings could be reviewed for potential improvements to support homebuyers.
- Policy Gaps: Existing programs often overlook the needs of those with lower incomes and limited savings, leaving many still unable to enter the housing market.
To effectively tackle the affordability crisis, more significant policy changes are needed. These could include reducing down payment requirements for first-time homebuyers, introducing innovative shared equity schemes, or expanding and enhancing existing assistance programs to cater to a wider range of incomes.
Alternatives and Solutions to the High Down Payment Barrier
Innovative solutions are needed to overcome the high down payment barrier and promote greater housing affordability.
- Shared Equity Programs: Expanding and improving shared equity programs, where the government or other institutions share the equity of a home, can allow buyers to enter the market with smaller down payments.
- Rent-to-Own Programs: Well-structured rent-to-own programs can offer a pathway to homeownership for those who might otherwise be excluded.
- Cooperative Housing: Encouraging the development of co-operative housing models can provide more affordable housing options.
- Increased Supply: Increasing the overall supply of affordable housing is crucial to alleviate demand pressures and bring down home prices.
By exploring and implementing such alternatives, Canada can move towards a more equitable and accessible housing market for all its citizens.
Conclusion
High down payments are a significant factor exacerbating the Canadian housing crisis. This problem is amplified by high mortgage rates and the limitations of current government policies. The consequence is limited homeownership for many Canadians and a widening income inequality gap. Addressing this crisis requires a multi-pronged approach that reduces the burden of high down payments, increases overall affordability, and fosters sustainable homeownership for all Canadians. Understanding the role of high down payments in this crisis is the first step toward finding effective solutions and creating a more accessible housing market. Let's continue the conversation and work towards a more just and equitable system.

Featured Posts
-
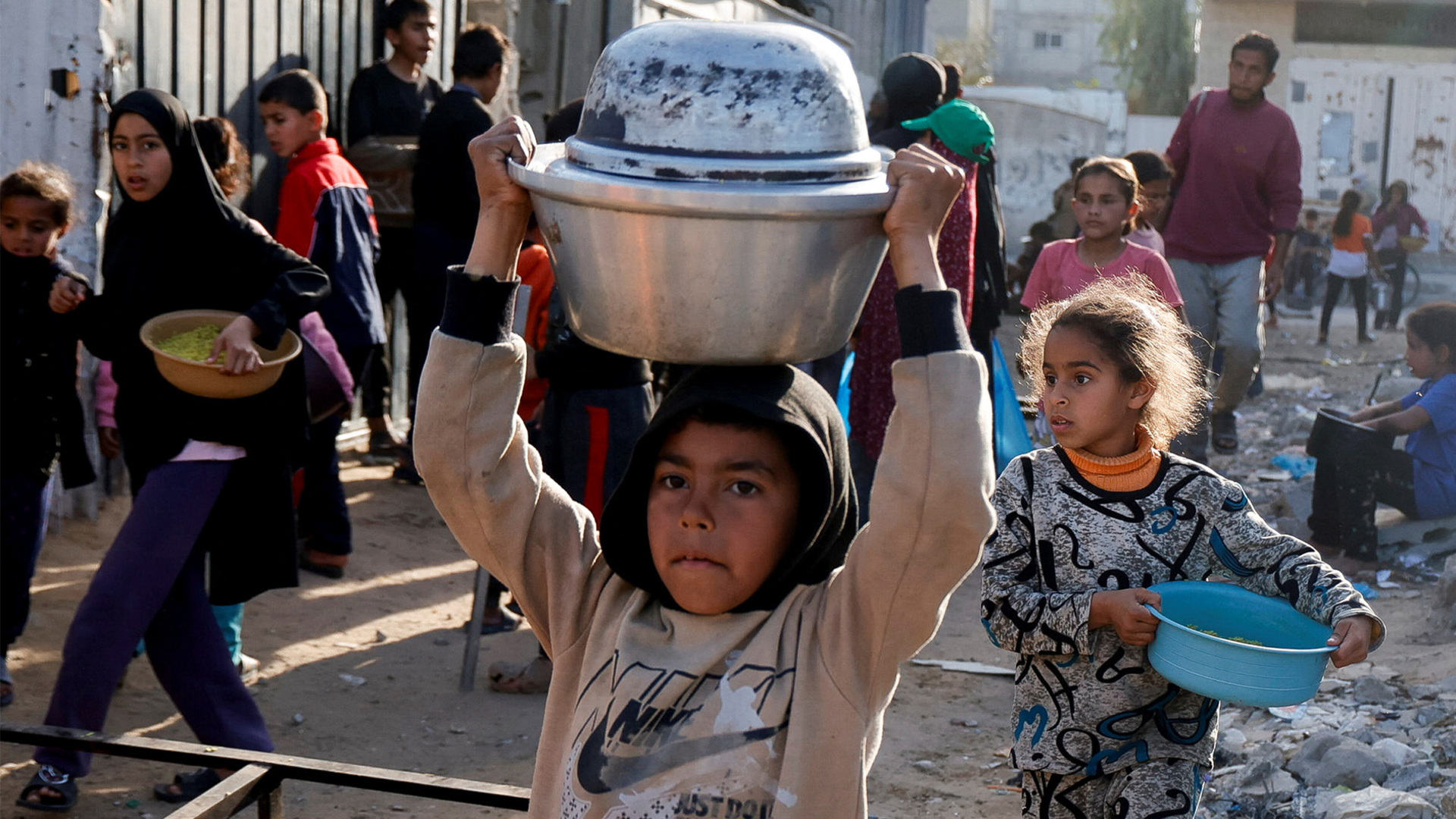 Life Under Blockade Examining Hunger Disease And Crime In Gaza
May 10, 2025
Life Under Blockade Examining Hunger Disease And Crime In Gaza
May 10, 2025 -
 Massive Fentanyl Seizure Details From Pam Bondis Announcement
May 10, 2025
Massive Fentanyl Seizure Details From Pam Bondis Announcement
May 10, 2025 -
 The Trump Factor Shifting Dynamics Between Greenland And Denmark
May 10, 2025
The Trump Factor Shifting Dynamics Between Greenland And Denmark
May 10, 2025 -
 Pakistan Sri Lanka And Bangladesh To Strengthen Capital Market Ties
May 10, 2025
Pakistan Sri Lanka And Bangladesh To Strengthen Capital Market Ties
May 10, 2025 -
 Operation Sindoor Fallout Kse 100 Trading Suspended Amidst Sharp Decline
May 10, 2025
Operation Sindoor Fallout Kse 100 Trading Suspended Amidst Sharp Decline
May 10, 2025
