The Future Of Electric Vehicles In California: The Impact Of The EV Mandate
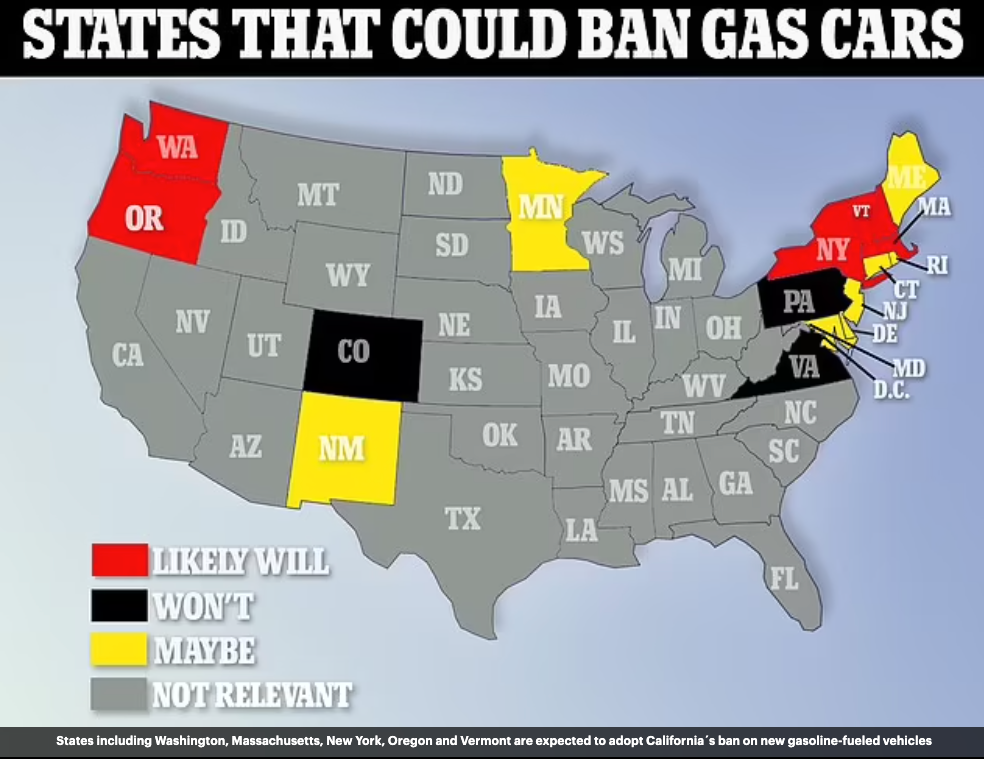
Table of Contents
Accelerated EV Adoption and its Challenges
California's EV mandate is projected to lead to a dramatic surge in electric vehicle sales over the coming years. This accelerated adoption, however, presents several significant challenges.
Infrastructure Development
The widespread adoption of EVs requires a robust and accessible charging infrastructure. This means a significant expansion of both public and private charging stations, including a substantial increase in fast-charging networks. Current infrastructure falls short of projected demand, creating potential bottlenecks. Addressing this requires:
- Increased investment in public charging stations: Focusing on strategic locations like highways, shopping centers, and apartment complexes.
- Incentivizing private sector investment: Offering tax breaks and subsidies to businesses installing charging stations.
- Smart grid integration: Implementing smart charging technologies to optimize energy distribution and minimize strain on the grid.
- Developing standardized charging connectors: Ensuring compatibility across different EV models and charging networks.
Affordability and Accessibility
A major barrier to EV adoption is the price disparity between electric vehicles and their gasoline-powered counterparts. While battery prices are decreasing, EVs still often carry a higher upfront cost. Government incentives, such as tax credits and rebates (EV incentives, electric vehicle subsidies), play a crucial role in bridging this affordability gap. However, the effectiveness of these incentives varies depending on income levels and vehicle types. Addressing affordability requires:
- Expanding and enhancing existing EV incentives: Making them more accessible to a wider range of consumers.
- Investing in affordable EV models: Supporting the development and production of lower-cost electric vehicles.
- Addressing the issue of used EV market accessibility: Ensuring that affordable used EVs are available to lower-income consumers.
Electricity Grid Capacity
The mass adoption of electric vehicles will inevitably place a strain on California's electricity grid. Charging millions of EVs simultaneously could lead to power outages and grid instability. Solutions involve:
- Investing in renewable energy sources: Increasing the proportion of electricity generated from solar, wind, and other renewable sources.
- Implementing smart grid technologies: Utilizing smart charging systems that optimize energy consumption and reduce peak demand.
- Upgrading existing grid infrastructure: Expanding transmission lines and improving grid reliability.
Environmental Impact and Emission Reductions
The primary goal of California's EV mandate is to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality. The transition to electric vehicles is expected to lead to a substantial decrease in the carbon footprint of transportation, resulting in:
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: Significantly lowering California's contribution to climate change. This will have a positive effect on the state's overall carbon footprint.
- Improved air quality: Decreasing air pollution in urban areas, leading to better public health outcomes. The reduction in air pollution will be particularly noticeable in densely populated cities.
- Reduced reliance on fossil fuels: Decreasing California's dependence on imported oil and reducing its vulnerability to oil price fluctuations.
The effectiveness of the mandate in achieving these environmental goals will depend on the speed of EV adoption, the expansion of renewable energy sources, and the overall efficiency of the electricity grid.
Economic Implications for California
California's EV mandate is not only an environmental policy but also an economic one. The transition to electric vehicles is expected to create numerous economic opportunities, including:
- Job creation in the EV sector: Generating employment in EV manufacturing, battery production, charging infrastructure development, and related industries. This includes jobs in both the manufacturing and service sectors. Increased EV manufacturing jobs will be a significant contributor to the state's economy.
- Economic growth in related industries: Boosting innovation and investment in clean energy technologies and supporting businesses.
- Attracting investment in California: Positioning the state as a leader in the global EV market and attracting investment from both domestic and international companies.
However, the transition also presents potential economic challenges, such as job losses in the traditional automotive industry and the need for significant infrastructure investment.
The Influence of California's Mandate on Other States
California's EV mandate is not just a state-level policy; it has national and even international implications. Its success (or challenges) will likely influence:
- Other states' EV policies: Inspiring other states to adopt similar or more stringent EV regulations. Many states are already adopting their own EV mandates, influenced by California's leadership.
- National EV policy: Potentially influencing the development of a national EV policy or standardized regulations across the United States. The federal government is increasingly considering national-level incentives and regulations for electric vehicles.
- Global EV adoption: Serving as a model for other countries looking to reduce emissions and transition to cleaner transportation systems.
Conclusion: The Future of Electric Vehicles in California and Beyond
California's EV mandate is a bold and ambitious undertaking with far-reaching consequences. Its success in accelerating electric vehicle adoption, reducing emissions, and stimulating economic growth will depend on overcoming several key challenges related to infrastructure development, affordability, and grid capacity. The mandate's influence extends beyond California's borders, potentially shaping national and even international EV policies. Stay informed about the future of electric vehicles in California and how the EV mandate continues to shape the landscape of sustainable transportation. Learn more about available EV incentives and contribute to a cleaner future!

Featured Posts
-
 Resultats Credit Mutuel Am Analyse De La Saison Des Resultats Du T4 2024
May 19, 2025
Resultats Credit Mutuel Am Analyse De La Saison Des Resultats Du T4 2024
May 19, 2025 -
 This Weeks Wine Selection Il Palagio Four Seasons Firenze
May 19, 2025
This Weeks Wine Selection Il Palagio Four Seasons Firenze
May 19, 2025 -
 Mairon Santos Ufc 313 Knockout Pursuit For 50 K Diaper Bonus
May 19, 2025
Mairon Santos Ufc 313 Knockout Pursuit For 50 K Diaper Bonus
May 19, 2025 -
 Pargs Armenian Eurovision Song Survivor Gets A Lyric Makeover
May 19, 2025
Pargs Armenian Eurovision Song Survivor Gets A Lyric Makeover
May 19, 2025 -
 Finding The Connections Nyt Puzzle 645 Hints And Solutions March 17
May 19, 2025
Finding The Connections Nyt Puzzle 645 Hints And Solutions March 17
May 19, 2025
