The Persistence Of Toxic Chemicals In Buildings Following The Ohio Train Derailment
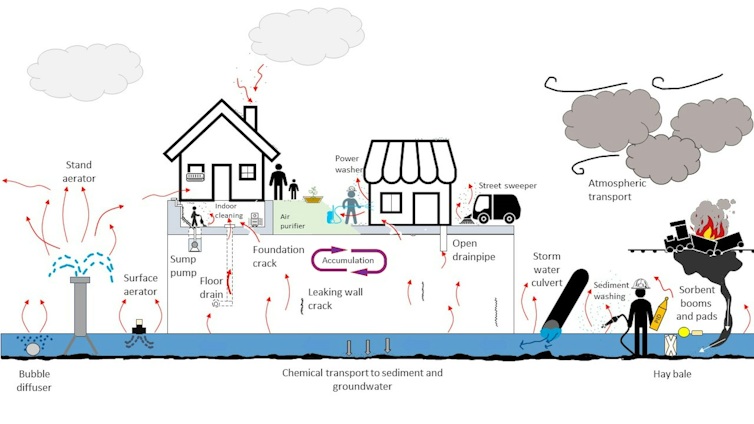
Table of Contents
H2: Types of Toxic Chemicals Released and Their Persistence
The derailment released a cocktail of hazardous substances, many of which are known for their persistence in the environment and their ability to infiltrate building materials. Understanding the properties of these chemicals is crucial to effective remediation.
H3: Vinyl Chloride and its Properties
Vinyl chloride, a known carcinogen, is particularly concerning due to its volatility and its tendency to persist in porous materials.
- Seeping into Building Materials: Vinyl chloride readily penetrates materials like wood, drywall, and insulation, becoming trapped within their structures.
- Long-Term Off-gassing: Even after the initial release, vinyl chloride can continue to off-gas slowly, resulting in prolonged exposure for building occupants. Studies from the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) detail this phenomenon.
- Difficult Removal: Complete removal of vinyl chloride from contaminated materials is extremely challenging and often requires specialized techniques.
H3: Other Persistent Contaminants
Beyond vinyl chloride, other chemicals released during the derailment pose significant risks. These include butyl acrylate, ethylene glycol monobutyl ether, and ethylhexyl acrylate.
- Butyl Acrylate: This chemical is known for its irritating properties and potential for respiratory problems. Its persistence varies depending on the material it contaminates.
- Ethylene Glycol Monobutyl Ether: This solvent can be absorbed through the skin and is associated with kidney and liver damage. It's relatively volatile, but residues may remain in certain building materials.
- Ethylhexyl Acrylate: This monomer can cause skin and eye irritation, and its persistence can vary widely.
H3: The Role of Building Materials in Chemical Retention
Different building materials exhibit varying capacities for absorbing and retaining toxic chemicals.
- Porous Materials: Materials like wood and drywall are highly porous and readily absorb chemicals, acting as reservoirs for long-term release.
- Less Porous Materials: Concrete and some types of insulation are less porous but can still retain contaminants on their surfaces or within micro-cracks.
- Material-Specific Remediation: Remediation strategies must consider the specific properties of each building material to ensure effective contaminant removal.
H2: Health Risks Associated with Long-Term Exposure
Exposure to the toxic chemicals released in the Ohio train derailment presents significant health risks, both acute and chronic.
H3: Acute and Chronic Health Effects
- Vinyl Chloride: Exposure can lead to liver cancer, brain tumors, and various other cancers. The National Cancer Institute provides extensive information on vinyl chloride's carcinogenic effects.
- Other Chemicals: Other released chemicals can cause respiratory problems, skin irritation, eye irritation, kidney damage, liver damage, and neurological effects, depending on the level and duration of exposure.
H3: Vulnerable Populations
Certain populations are particularly vulnerable to the health effects of these chemicals.
- Children: Their developing bodies are more susceptible to the toxic effects.
- Elderly: Pre-existing health conditions may exacerbate the impact of chemical exposure.
- Individuals with Pre-existing Conditions: Those with respiratory or immune system problems are at increased risk.
H3: Difficulty in Diagnosing Long-Term Effects
Diagnosing long-term health problems resulting from low-level exposure to multiple toxins is challenging.
- Multiple Chemical Exposure: The mixture of chemicals makes it difficult to attribute specific health issues to a single substance.
- Delayed Onset: Some health problems may not manifest until years after exposure.
H2: Remediation and Mitigation Strategies
Effective remediation and mitigation strategies are crucial to protect the health and safety of those affected.
H3: Professional Cleaning and Decontamination
Professional remediation services are essential. Techniques include:
- Air Scrubbing: Removing contaminated air from buildings.
- Surface Cleaning: Thorough cleaning of surfaces to remove chemical residues.
- Material Removal: In severe cases, removing and replacing heavily contaminated materials may be necessary.
H3: Air Quality Monitoring
Continuous air quality monitoring is critical to assess the effectiveness of remediation and ensure long-term safety.
- Short-Term Monitoring: Immediately following remediation to ensure effectiveness.
- Long-Term Monitoring: Ongoing monitoring to detect any resurgence of contamination.
H3: Governmental Regulations and Assistance
Government agencies play a crucial role in providing guidance, resources, and assistance.
- EPA: The Environmental Protection Agency provides guidance on remediation and cleanup.
- State and Local Agencies: Provide support and resources to affected communities.
- Financial Assistance: Government programs may offer financial assistance for remediation efforts.
3. Conclusion
The persistence of toxic chemicals in buildings following the Ohio train derailment poses a significant and ongoing threat to environmental health and public safety. The potential for long-term health consequences highlights the critical need for thorough remediation, continuous air quality monitoring, and proactive government support. Addressing persistent chemical contamination requires a multifaceted approach involving professional decontamination, vigilant monitoring, and ongoing community engagement. If you suspect building contamination from the derailment, seek professional assessment and remediation immediately. Contact your local health department and relevant government agencies for information and assistance concerning the long-term effects of toxic chemicals and available resources for building decontamination following the Ohio train derailment. Through collective effort and responsible action, we can strive to ensure the health and safety of affected communities and pave the way for a successful recovery.

Featured Posts
-
 Communique De Presse Amf Seb Sa 2025 E1021792 24 Fevrier 2025
Apr 30, 2025
Communique De Presse Amf Seb Sa 2025 E1021792 24 Fevrier 2025
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Disney Layoffs Nearly 200 Abc News Staffers Affected
Apr 30, 2025
Disney Layoffs Nearly 200 Abc News Staffers Affected
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Blue Ivy Carters Super Bowl Style A Fan Favorite
Apr 30, 2025
Blue Ivy Carters Super Bowl Style A Fan Favorite
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Il Risarcimento Di Becciu La Beffa Dopo Il Danno Per Le Vittime
Apr 30, 2025
Il Risarcimento Di Becciu La Beffa Dopo Il Danno Per Le Vittime
Apr 30, 2025 -
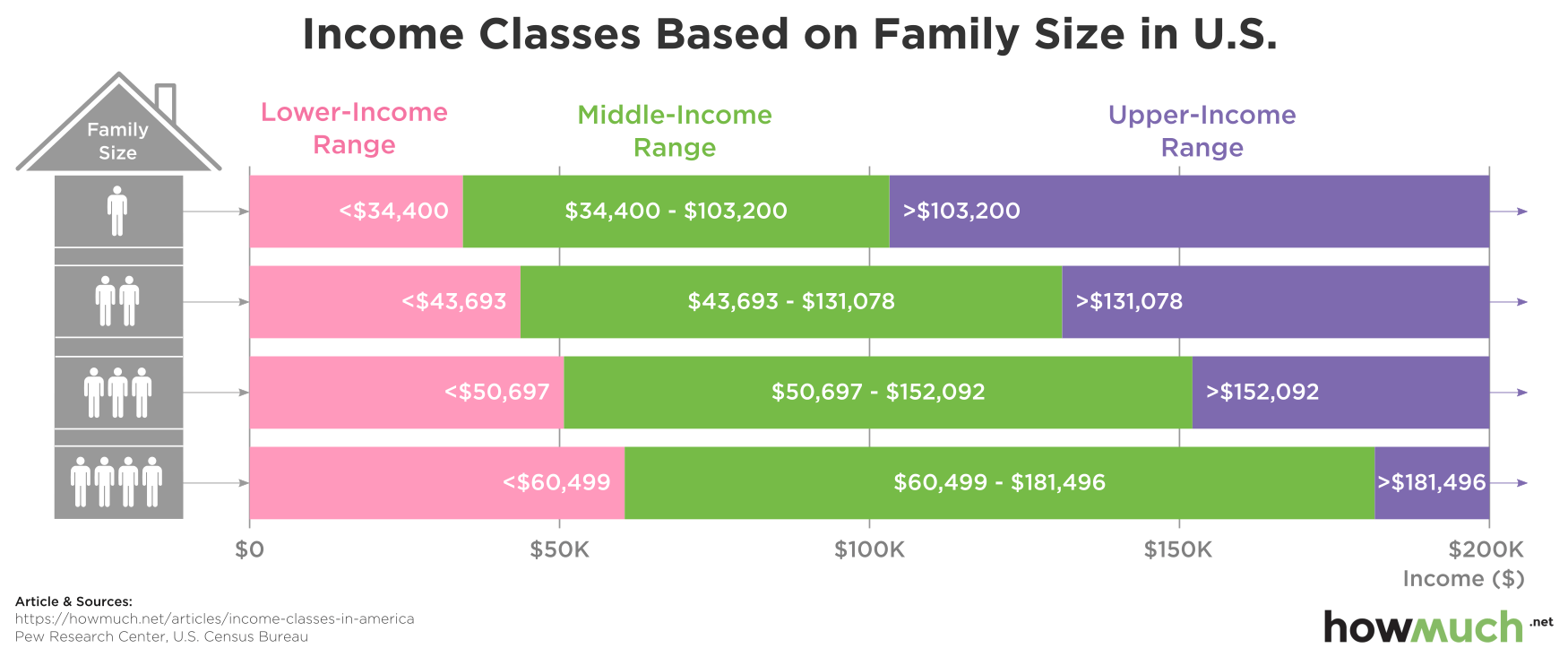 Us Middle Class Income A State By State Breakdown
Apr 30, 2025
Us Middle Class Income A State By State Breakdown
Apr 30, 2025
