The Rising Threat Of Wildfires: Driving Record Levels Of Global Forest Loss
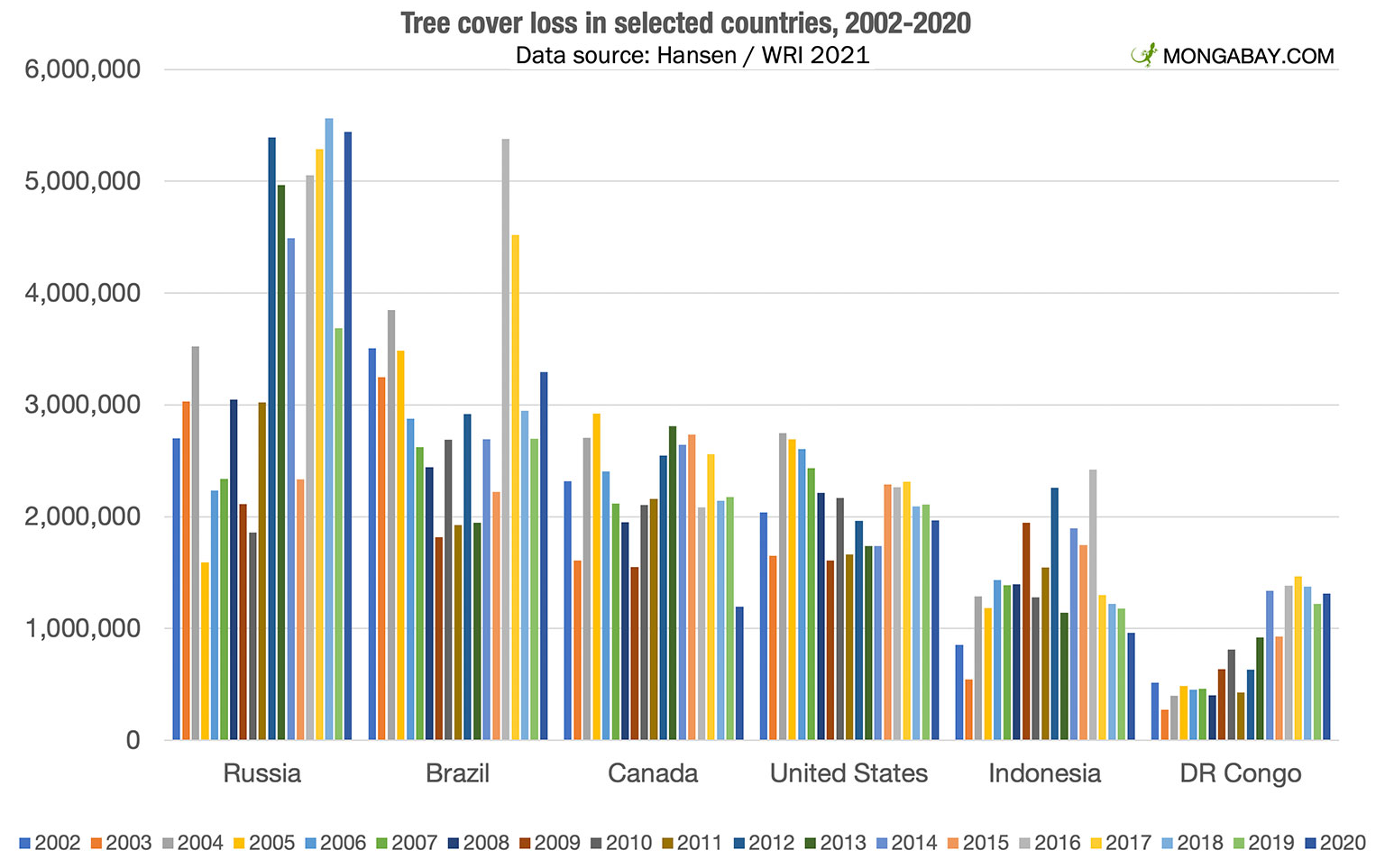
Table of Contents
H2: The Escalating Frequency and Intensity of Wildfires
H3: Climate Change as a Primary Driver
Climate change is undeniably fueling the wildfire crisis. Rising global temperatures, prolonged droughts, and altered weather patterns create ideal conditions for ignition and rapid fire spread. Data from numerous sources show a strong correlation between increasing average temperatures and the frequency and severity of wildfires globally. For example, the western United States, Australia, and parts of the Amazon rainforest have experienced record-breaking wildfire seasons in recent years, directly linked to sustained periods of extreme heat and drought.
- Rising global temperatures increase dry vegetation: Warmer temperatures lead to drier vegetation, turning forests and grasslands into tinderboxes.
- Longer, more intense droughts create tinder-dry conditions: Prolonged droughts significantly reduce soil moisture and vegetation moisture content, making landscapes highly susceptible to ignition.
- Changes in wind patterns can spread fires rapidly: Stronger and more unpredictable winds can rapidly spread wildfires over vast distances, making containment significantly more challenging.
H3: Human Activities Contributing to the Problem
While climate change is a major factor, human activities significantly contribute to the escalating wildfire problem. Human negligence, such as unattended campfires and discarded cigarettes, remains a leading cause of forest fires. Furthermore, deforestation and unsustainable land management practices increase the risk and severity of wildfires. The expansion of urban areas into wildland-urban interfaces (WUI) also creates more opportunities for wildfires to spread into populated areas.
- Arson and accidental human ignitions: Deliberately set fires and accidents contribute significantly to the number of wildfires each year.
- Expansion of urban areas into wildland-urban interfaces (WUI): Homes built near forests create a higher risk of fires spreading into populated areas.
- Inadequate forest management practices: Poor forest management, such as insufficient forest thinning and the lack of controlled burns, leads to increased fuel loads.
H2: Devastating Consequences of Wildfires on Global Forest Loss
H3: Biodiversity Loss and Habitat Destruction
Wildfires cause catastrophic biodiversity loss. The destruction of habitats leads to population declines and even extinction of numerous plant and animal species. The long-term consequences for ecosystem health and resilience are profound, impacting intricate ecological processes and disrupting food chains. Many endangered species are particularly vulnerable to wildfires, further jeopardizing their survival.
- Loss of crucial habitats for numerous species: Wildfires destroy vital habitats, forcing animals to relocate or face starvation and death.
- Disruption of ecological processes: Wildfires alter the natural balance of ecosystems, impacting nutrient cycles and species interactions.
- Extinction of plant and animal species: The loss of habitat and resources can drive vulnerable species to extinction.
H3: Carbon Emissions and Climate Feedback Loops
Wildfires release massive amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, significantly contributing to climate change. This creates a dangerous positive feedback loop: climate change increases wildfire risk, and wildfires exacerbate climate change. The destruction of forests, which act as crucial carbon sinks, further accelerates global warming.
- Significant contribution to global greenhouse gas emissions: Wildfires are a major source of CO2 and other greenhouse gases, fueling climate change.
- Loss of carbon sinks, further accelerating climate change: Burned forests lose their ability to absorb CO2, worsening the climate crisis.
- Impact on air quality and human health: Smoke from wildfires causes severe air pollution, impacting respiratory health and leading to numerous health issues.
H3: Economic and Social Impacts
The economic and social costs of wildfires are immense. Fighting wildfires is incredibly expensive, and property damage and loss of livelihoods are widespread. Communities are displaced, local economies are crippled, and tourism industries suffer. The psychological impacts on affected populations are also severe, resulting in long-term trauma and mental health challenges.
- Property damage and loss of livelihoods: Homes, businesses, and infrastructure are destroyed, leaving many without homes or jobs.
- Disruption of infrastructure and services: Wildfires damage roads, power lines, and communication networks, disrupting essential services.
- Mental health impacts on affected communities: The trauma of experiencing a wildfire can have lasting mental health consequences.
H2: Mitigation and Prevention Strategies
H3: Improved Forest Management Practices
Effective forest management is crucial for mitigating wildfire risk. This includes implementing controlled burns to reduce fuel loads, thinning forests to create firebreaks, and improving early detection and rapid response systems. Sustainable forestry practices are essential for maintaining healthy and resilient forests less susceptible to severe wildfires.
- Prescribed burns to reduce fuel load: Controlled burning helps reduce the amount of dry vegetation, lessening the intensity and spread of wildfires.
- Improved forest thinning and management: Strategic thinning reduces fuel density and creates firebreaks to slow fire spread.
- Early detection and suppression strategies: Investing in advanced technology and training for early detection and rapid response is critical.
H3: Climate Change Mitigation
Addressing the root cause of increased wildfire risk—climate change—is paramount. This requires global cooperation to reduce greenhouse gas emissions through a transition to renewable energy sources, improvements in energy efficiency, and sustainable transportation systems. International agreements and collaborative efforts are essential for effective climate action.
- Transition to renewable energy sources: Shifting away from fossil fuels to clean energy sources is crucial in reducing emissions.
- Reduction of carbon emissions from transportation: Improving transportation efficiency and promoting electric vehicles will lower emissions.
- Global collaboration on climate action: International cooperation is essential to effectively address climate change.
H3: Public Awareness and Education
Public awareness and education play a critical role in preventing human-caused wildfires. Fire safety regulations must be enforced, and responsible behavior in wildland areas must be promoted. Educational campaigns can empower individuals to make informed choices and contribute to wildfire prevention.
- Public awareness campaigns on fire safety: Educating the public about safe campfire practices and the risks of discarded cigarettes.
- Enforcement of fire prevention regulations: Strict enforcement of fire regulations helps prevent careless acts that can start fires.
- Community engagement and education programs: Engaging communities in fire prevention efforts builds awareness and fosters responsibility.
3. Conclusion
The escalating threat of wildfires and the resulting global forest loss demand immediate and concerted action. We have explored the intricate relationship between climate change and human activities in driving the increasing frequency and intensity of wildfires. The devastating consequences for biodiversity, climate, and human societies underscore the urgency of implementing effective mitigation and prevention strategies. By understanding the causes and consequences of these devastating events, and by actively participating in prevention and mitigation efforts, we can collectively work towards protecting our forests and safeguarding our planet. Let's combat the rising threat of wildfires together. Support organizations dedicated to wildfire prevention, advocate for robust climate action policies, and practice responsible behavior in wildland areas to protect our forests for future generations.

Featured Posts
-
 Maxine Transformation Affronter Demain Avec Confiance
May 23, 2025
Maxine Transformation Affronter Demain Avec Confiance
May 23, 2025 -
 Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 97 1 Double Q Key Findings And Interpretations
May 23, 2025
Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 97 1 Double Q Key Findings And Interpretations
May 23, 2025 -
 The Impact Of Slowing Growth Sse Cuts Spending By 3 Billion
May 23, 2025
The Impact Of Slowing Growth Sse Cuts Spending By 3 Billion
May 23, 2025 -
 Sam Cook Englands New Test Bowler For Zimbabwe Series
May 23, 2025
Sam Cook Englands New Test Bowler For Zimbabwe Series
May 23, 2025 -
 China And Us Trade Record Exports Before Potential Truce
May 23, 2025
China And Us Trade Record Exports Before Potential Truce
May 23, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Unexpected Joe Jonas Concert Thrills Fort Worth Stockyards Crowd
May 23, 2025
Unexpected Joe Jonas Concert Thrills Fort Worth Stockyards Crowd
May 23, 2025 -
 Fort Worth Stockyards An Unforgettable Night With Joe Jonas
May 23, 2025
Fort Worth Stockyards An Unforgettable Night With Joe Jonas
May 23, 2025 -
 Dc Legends Of Tomorrow Frequently Asked Questions And Answers
May 23, 2025
Dc Legends Of Tomorrow Frequently Asked Questions And Answers
May 23, 2025 -
 The Last Rodeo Exploring Neal Mc Donoughs Character
May 23, 2025
The Last Rodeo Exploring Neal Mc Donoughs Character
May 23, 2025 -
 A Deep Dive Into Dc Legends Of Tomorrow
May 23, 2025
A Deep Dive Into Dc Legends Of Tomorrow
May 23, 2025
