Eurovision's Voting System: Rules And Regulations
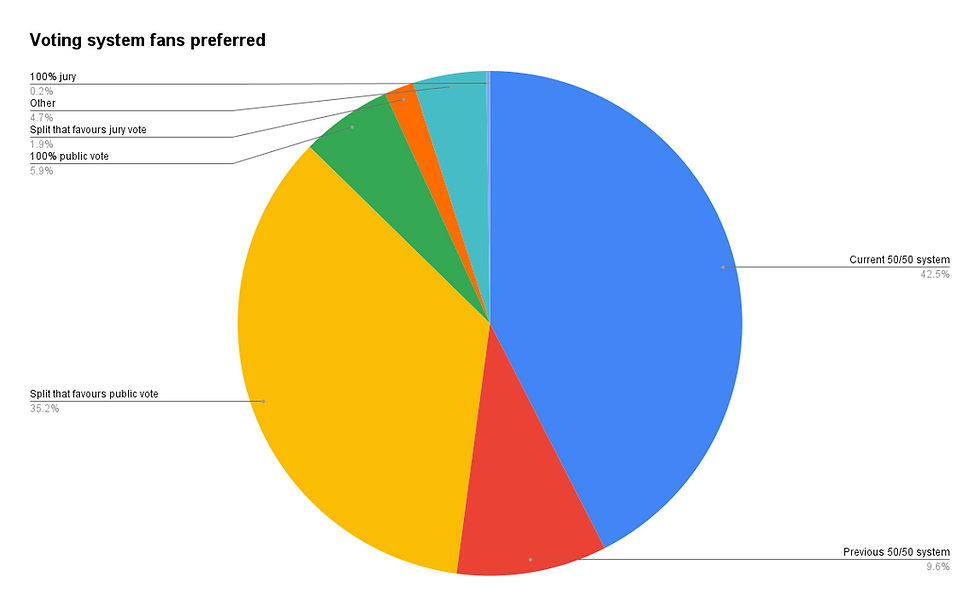
Table of Contents
The Two-Stage Voting Process
The Eurovision Song Contest utilizes a two-part voting system to determine the winner: Jury voting and public televoting. This dual approach aims to balance expert opinion with popular preference, creating a more comprehensive and representative outcome.
Jury Voting
National juries, comprised of five music professionals from each participating country, play a significant role in the Eurovision voting system. These juries are carefully selected to ensure diversity of musical expertise and background, promoting impartiality and preventing potential bias. Their anonymity is strictly maintained throughout the process to avoid external influence or pressure.
Each jury member independently scores each participating song, awarding points according to a pre-determined scale: 1-8, 10, and 12 points. The scores are then aggregated to produce a national jury ranking. Preventing collusion and ensuring fairness is paramount; therefore, rigorous measures are in place. This includes:
- Random jury selection: Juries are chosen through a process designed to minimize bias and ensure a diverse representation of musical perspectives.
- Secret ballots: Individual jury scores remain confidential until the official announcement, preventing external pressure and manipulation.
- Independent verification: The entire jury voting process undergoes independent verification to ensure accuracy and integrity.
While measures are in place to mitigate bias, the potential for subjective interpretation always exists. However, the diversity of the jury and the independent verification processes are designed to minimize any significant impact.
Public Televoting
The public plays an equally important role in the Eurovision voting system via televoting. Viewers in each participating country can vote for their favorite songs using various methods: telephone, dedicated mobile applications, and SMS text messages. These votes are tallied independently by specialized companies employing secure voting platforms, with strict measures in place to prevent fraud.
Significant safeguards exist to ensure the integrity of the public vote:
- Secure voting platforms: Robust technological systems are used to minimize vulnerabilities and prevent fraudulent voting activity.
- Vote limits per number: Restrictions are implemented to prevent individual voters from disproportionately influencing the results through multiple votes.
- Fraud detection mechanisms: Sophisticated algorithms are employed to identify and filter out potentially fraudulent votes, ensuring fair and accurate results.
Point Allocation and Calculation
The final Eurovision ranking is determined by combining the points awarded by the national juries and the public televote. Historically, the weighting of jury and public votes has varied; however, currently, both contribute equally to the final score.
Each country's jury and public votes are tallied separately, and then these are combined to give a total score for each participating country. A hypothetical example: if Country A receives 100 points from the juries and 80 points from the public, their total score would be 180 points. The country with the highest combined score is declared the winner.
In cases of a tie, specific tie-breaker procedures are in place, often involving a detailed review of the individual jury and public scores to identify the winning entry. Transparency in the results announcement is a key principle of the Eurovision voting system. Specific details regarding this process are published by the European Broadcasting Union (EBU).
- Weighted average calculation: A weighted average calculation is used to ensure both jury and public opinion contribute to the final scores (the exact weighting can vary year-to-year).
- Tie-breaker procedures: Clear protocols are in place to resolve any ties in the final standings.
- Transparency in results announcement: The EBU ensures the entire process is transparent, clearly explaining the point allocation and calculation.
Rules and Regulations Regarding Voting Eligibility
Eligibility to vote in the Eurovision Song Contest is subject to specific rules and regulations designed to ensure fairness and prevent manipulation. Generally, only residents of participating countries are permitted to vote. This is to prevent external influence on the contest's outcome.
Restrictions on voting often include limits on the number of votes per telephone number or individual to prevent any single voter from unduly influencing the results. Penalties for irregularities, including fraudulent voting, are also clearly outlined, with severe consequences ranging from disqualification to legal action.
- Geographic restrictions: Only residents of participating countries are eligible to vote.
- Age restrictions: Minimum age requirements are often in place (typically 16 years old).
- Penalties for fraudulent voting: Strict measures are taken to prevent and punish attempts to manipulate the voting process.
Changes and Evolution of the Eurovision Voting System
The Eurovision Voting System has undergone several significant changes throughout its history. These modifications aim to continuously improve fairness, transparency, and accuracy. For example, the introduction of televoting modernized the voting process and increased audience engagement. The weighting of jury versus public votes has also been adjusted in various iterations to balance expert opinion and popular preference.
These changes reflect the EBU's ongoing commitment to refining the system and addressing any potential issues or irregularities that may arise. The impact of these modifications has been notable, resulting in a more balanced and dynamic competition.
- Historical changes to the voting system: From postcard voting to the current sophisticated digital systems, significant advancements have been made.
- Reasons for system updates: The EBU constantly reviews and updates the system to maintain fairness and adapt to technological advancements.
- Impacts of modifications: Changes have significantly influenced the overall dynamic of the competition, promoting greater fairness and inclusivity.
Conclusion:
The Eurovision Voting System, with its combination of jury and public voting, aims for a balance between expert opinion and popular appeal. While it has undergone several evolutions to enhance fairness and transparency, understanding its intricacies reveals a fascinating process that contributes significantly to the drama and excitement of the Eurovision Song Contest. To further explore the complexities and history of this captivating process, continue your research on the Eurovision Voting System and stay updated on any rule changes for upcoming contests.

Featured Posts
-
 First Class Mail Delays Royal Mail Announces Potential Price Hikes
May 19, 2025
First Class Mail Delays Royal Mail Announces Potential Price Hikes
May 19, 2025 -
 Eurowizja Steczkowska Ocena Fanow I Komentarze Po Konkursie
May 19, 2025
Eurowizja Steczkowska Ocena Fanow I Komentarze Po Konkursie
May 19, 2025 -
 Instalaciones Del Cne Blindadas Por La Policia Nacional En La Capital
May 19, 2025
Instalaciones Del Cne Blindadas Por La Policia Nacional En La Capital
May 19, 2025 -
 Living With A High Earning Spouse A Stars Experience
May 19, 2025
Living With A High Earning Spouse A Stars Experience
May 19, 2025 -
 Austria Wins Eurovision 2025 With Jjs Powerful Ballad Wasted Love
May 19, 2025
Austria Wins Eurovision 2025 With Jjs Powerful Ballad Wasted Love
May 19, 2025
