Is Netflix A Tariff Haven? Examining Its Performance Against Big Tech
Table of Contents
Netflix's Global Content Distribution Model and Tariff Implications
Netflix's success hinges on its ability to deliver engaging content globally. Its sophisticated content distribution model significantly impacts its tariff exposure.
Content Localization and Production
Netflix actively invests in localized content production. Instead of solely relying on US-produced content, it commissions shows and films in various countries, reducing reliance on costly imports and associated tariffs.
- Examples: "Squid Game" (South Korea), "Money Heist" (Spain), "Lupin" (France). These local productions minimize import duties and resonate more strongly with local audiences.
- Licensing Agreements: Netflix also strategically licenses content from international producers, navigating complex licensing agreements and tariff structures on a case-by-case basis. This allows them to acquire content at potentially lower costs than importing and distributing solely from the US.
- Impact on Import/Export Duties: By producing locally, Netflix significantly reduces the import duties associated with bringing foreign content into various markets. This is a key element of its tariff minimization strategy.
Data Centers and Infrastructure
Netflix's global network of data centers plays a crucial role in its tariff strategy. Strategically positioning these centers in multiple countries minimizes data transfer costs and potential tariffs associated with transborder data flows.
- Location of Data Centers: Netflix strategically places its data centers in various regions globally, ensuring content is served from servers geographically closer to its users. This reduces latency and minimizes the need for expensive, long-distance data transfers which could attract tariffs.
- Cost Savings: Localizing data centers reduces both latency and costs associated with international data transmission and potential tariffs.
- Compliance with Local Regulations: The presence of local data centers helps Netflix comply with regional regulations regarding data storage and processing, potentially mitigating regulatory risks and associated financial penalties.
- Potential Tariff Avoidance Strategies: While not directly avoiding tariffs, the strategic placement of data centers reduces the volume of data that needs to cross international borders, thus indirectly lowering potential tariff liabilities.
Streaming vs. Physical Media
The shift to streaming has dramatically altered the landscape of content distribution, and its impact on tariffs is significant.
- Tariffs on Physical Media: The distribution of physical media (DVDs, Blu-rays) is subject to import/export duties and various other trade taxes, impacting profitability.
- Import/Export Costs: Shipping physical media internationally involves significant logistical and cost burdens.
- Digital Distribution Advantages: Streaming allows Netflix to bypass these challenges; digital distribution is significantly less susceptible to tariffs associated with physical goods. The marginal cost of serving an additional subscriber is lower, improving profit margins.
Comparing Netflix's Tariff Exposure to Other Big Tech Companies
While Netflix's global strategy is impressive, comparing it to other Big Tech companies reveals nuanced differences in their tariff management approaches.
Amazon, Google, and Apple's Strategies
Amazon, Google, and Apple each employ unique global strategies impacting their tariff exposure.
-
Amazon: Amazon's diversified business (AWS, e-commerce) faces different tariff implications. AWS relies on global data centers similar to Netflix, while its retail arm faces tariffs on imported goods.
-
Google: Google's cloud services (similar to AWS) and hardware (Pixel phones, etc.) expose it to different tariff structures. Data center location and hardware manufacturing significantly impact their exposure.
-
Apple: Apple's reliance on hardware manufacturing in China exposes it to tariffs and potential supply chain disruptions significantly more than Netflix, which relies predominantly on digital content.
-
Key Differences & Similarities: While all companies utilize global infrastructure, their reliance on physical goods vs. digital services creates significant differences in tariff exposure. Netflix's digital-first model gives it a clear advantage in minimizing tariff impacts compared to its hardware-focused counterparts.
Tax Optimization and International Regulations
Tax optimization and international regulations play a vital role in the tariff strategies of these tech giants.
- Tax Haven Allegations: All these companies have faced scrutiny regarding their tax optimization strategies, employing legal means to minimize their tax burden in various jurisdictions. However, these strategies do not directly translate to tariff avoidance.
- Legal Compliance Issues: Navigating complex international tax laws and regulations is crucial for all these companies. Non-compliance can lead to significant financial penalties.
- Potential Criticisms of Aggressive Tax Minimization: Aggressive tax minimization strategies by these companies have drawn criticism from governments and the public, leading to increased regulatory scrutiny and calls for greater transparency.
The Future of Netflix and Tariff Strategies in the Global Marketplace
The future of Netflix's tariff strategy depends heavily on evolving geopolitical landscapes and technological advancements.
Geopolitical Risks and Regulatory Changes
- Trade Wars: Escalating trade tensions between countries could dramatically impact Netflix's operations. Tariffs on data transfers or content licensing could significantly impact profitability.
- New Regulations: Changes in international trade agreements and data privacy regulations could necessitate adjustments to its global infrastructure and content delivery strategy.
- Potential Disruptions to Global Supply Chains: Disruptions in global supply chains – as seen during the COVID-19 pandemic – can impact the availability of hardware and other resources needed for operations.
- Implications for Future Expansion: The political and economic climate will significantly influence future expansion plans and investment decisions.
The Evolution of Content Delivery and Tariff Avoidance
Emerging technologies offer new opportunities for minimizing tariff exposure.
- Benefits of Decentralized Content Delivery: Edge computing and content delivery networks (CDNs) allow for the distribution of content closer to users, reducing reliance on large, centralized data centers and potentially mitigating data transfer tariffs.
- Technological Advancements: Ongoing technological advancements in data compression and content delivery will further optimize efficiency and reduce reliance on international data transfers.
- Cost Savings Related to Reduced Reliance on Centralized Data Centers: By shifting toward decentralized content delivery, Netflix can potentially reduce costs associated with maintaining and securing a large number of centralized data centers globally.
Conclusion: Is Netflix Truly a Tariff Haven? A Final Analysis
Netflix's global strategy, characterized by localized content production and a globally distributed data center network, appears to effectively minimize its tariff exposure compared to other Big Tech companies with more significant reliance on physical goods. While not operating in traditional "tax havens," Netflix strategically leverages its digital-first model to reduce its vulnerability to import/export duties and international trade restrictions. Whether or not Netflix can be definitively labeled a "tariff haven" remains a matter of interpretation, but its strategic approach clearly demonstrates a commitment to minimizing its tariff liabilities. However, geopolitical uncertainty and regulatory changes remain significant risks to its future strategy. To further explore the complexities of international business strategies and tariff implications, we encourage you to delve deeper into resources such as government websites, academic research, and industry reports. Continue your research using keywords such as "Netflix tariff strategy," "Big Tech tax avoidance," or similar terms to broaden your understanding of how global corporations navigate the intricacies of the global market.

Featured Posts
-
 Obamacare Supreme Court Case Trumps Role And Rfk Jr S Potential Gain
Apr 22, 2025
Obamacare Supreme Court Case Trumps Role And Rfk Jr S Potential Gain
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Future Of Nordic Defense Collaboration Between Sweden And Finland
Apr 22, 2025
Future Of Nordic Defense Collaboration Between Sweden And Finland
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Ftcs Appeal Could Block Microsofts Activision Blizzard Acquisition
Apr 22, 2025
Ftcs Appeal Could Block Microsofts Activision Blizzard Acquisition
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Russias Easter Truce Ends Renewed Fighting In Ukraine
Apr 22, 2025
Russias Easter Truce Ends Renewed Fighting In Ukraine
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Subsystem Malfunction Forces Blue Origin To Cancel Rocket Launch
Apr 22, 2025
Subsystem Malfunction Forces Blue Origin To Cancel Rocket Launch
Apr 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
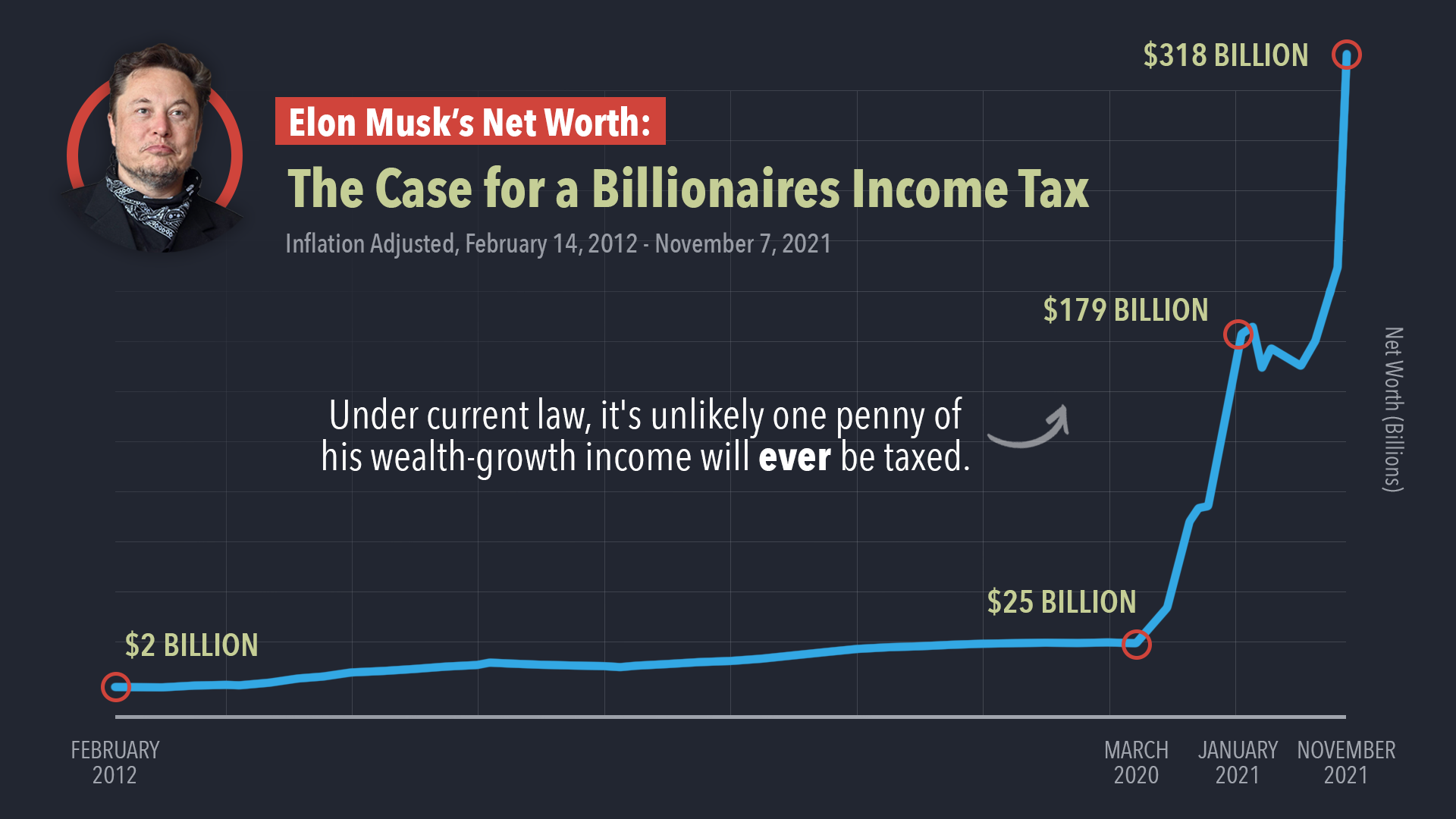 Examining The Relationship Between Us Economic Power And Elon Musks Wealth
May 10, 2025
Examining The Relationship Between Us Economic Power And Elon Musks Wealth
May 10, 2025 -
 Fluctuations In Elon Musks Net Worth Correlation With Us Economic Trends
May 10, 2025
Fluctuations In Elon Musks Net Worth Correlation With Us Economic Trends
May 10, 2025 -
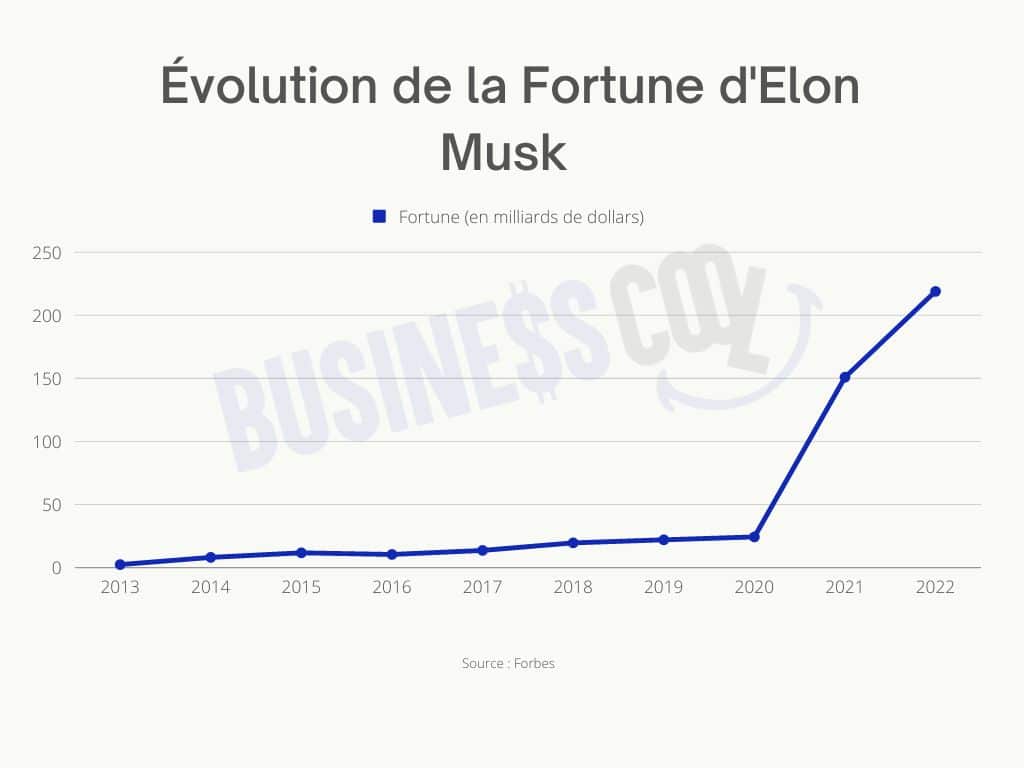 Teslas Success And Elon Musks Fortune An Examination Of Us Economic Factors
May 10, 2025
Teslas Success And Elon Musks Fortune An Examination Of Us Economic Factors
May 10, 2025 -
 Analyzing Elon Musks Net Worth The Role Of Us Economic Conditions
May 10, 2025
Analyzing Elon Musks Net Worth The Role Of Us Economic Conditions
May 10, 2025 -
 The Tesla Dogecoin Connection Analyzing The Recent Market Volatility
May 10, 2025
The Tesla Dogecoin Connection Analyzing The Recent Market Volatility
May 10, 2025
