OECD: Flat Growth For Canadian Economy In 2025, Recession Avoided
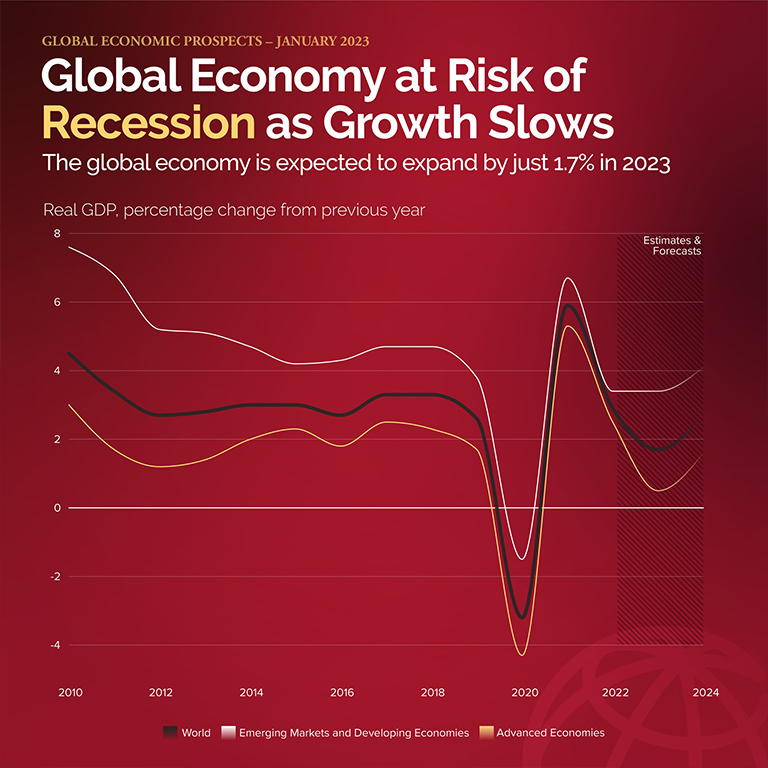
Table of Contents
Key Factors Contributing to Stagnant Growth
Several interconnected factors contribute to the OECD's prediction of stagnant Canadian economic growth in 2025.
Global Economic Uncertainty
The global economic landscape presents significant headwinds for Canada. Persistently high inflation in many countries, ongoing supply chain disruptions stemming from the pandemic and geopolitical events, and geopolitical instability, particularly the war in Ukraine, are creating a challenging international environment. This translates into weakening global demand for Canadian exports, impacting key sectors of the Canadian economy.
- Weakening global demand: Reduced international purchasing power is dampening export growth.
- Rising interest rates: Global central banks' efforts to combat inflation through interest rate hikes are impacting investment and consumer spending worldwide, including in Canada.
- Energy price volatility: Fluctuations in global energy prices continue to create uncertainty and impact both consumer and business costs. The OECD report estimates that these factors will contribute to a [Insert statistic from OECD report, e.g., "1.5% reduction"] in Canadian GDP growth in 2025.
High Interest Rates and Their Impact
The Bank of Canada's aggressive monetary policy tightening to curb inflation is another significant factor. Increased interest rates lead to higher borrowing costs for both businesses and consumers.
- Increased borrowing costs: Higher mortgage rates are cooling the housing market, a key driver of Canadian economic activity.
- Cooling housing market: Reduced housing activity translates into decreased construction and related spending.
- Impact on business investment: Higher borrowing costs make it more expensive for businesses to invest in expansion and new projects, slowing down job creation and economic growth. The Bank of Canada's projected interest rate for 2025 is [Insert predicted interest rate from a reliable source, e.g., "around 4%"].
Resilience of the Canadian Labor Market
Despite the economic headwinds, the Canadian labor market remains relatively strong, providing some cushioning against a sharper economic downturn.
- Low unemployment rate: Canada continues to boast a relatively low unemployment rate, indicating a robust job market.
- Robust employment growth in specific sectors: Certain sectors, such as technology and healthcare, continue to show strong employment growth, supporting consumer spending. This strength in the labor market is helping to maintain consumer spending, a crucial element of economic stability.
OECD Forecast Details and Implications
The OECD's forecast for Canadian GDP growth in 2025 is [Insert OECD's predicted GDP growth rate]. This represents a significant slowdown compared to [mention previous year's growth rate] but avoids a contraction, meaning a recession is averted, according to their projections.
GDP Growth Projection
[Insert a visual aid – chart or graph – showcasing the projected GDP growth for 2025 compared to previous years and other G7 nations. Ensure proper attribution to the OECD.] This relatively flat growth projection is significantly lower than growth rates observed in previous years, reflecting the global economic challenges mentioned above.
Potential Risks and Upside
While the OECD forecast predicts stagnant growth, several factors could alter this prediction.
- Unexpected global shocks: Further geopolitical instability or unforeseen global economic events could negatively impact the Canadian economy.
- Changes in commodity prices: Fluctuations in the prices of key Canadian exports, such as oil and minerals, significantly impact GDP.
- Government policy changes: Government fiscal or monetary policy decisions could influence the direction of economic growth. The forecast indicates a range of possible outcomes, suggesting that the actual growth rate could vary within a [mention percentage range] margin.
What the Forecast Means for Canadians
The OECD's forecast of flat economic growth has significant implications for both consumers and businesses across Canada.
Impact on Consumers
The projected flat growth will likely continue to exert pressure on household budgets.
- Inflationary pressures: High inflation will likely persist, eroding purchasing power.
- Wage growth: Wage growth may not keep pace with inflation, squeezing consumer spending.
- Consumer confidence: Uncertainty surrounding the economy may lead to decreased consumer confidence and reduced spending. This could affect savings and investment decisions, potentially leading individuals to prioritize short-term security over long-term investments.
Impact on Businesses
Businesses should anticipate a challenging environment, requiring adaptation and strategic planning.
- Impact on different sectors: The impact will vary across sectors. For example, the real estate sector may continue to experience slower growth, while the technology sector might see more resilience.
- Challenges and opportunities: Businesses will need to navigate higher borrowing costs and potential reduced consumer demand while also identifying opportunities in emerging sectors. Job creation may be slower, requiring businesses to focus on efficiency and productivity improvements.
Conclusion
The OECD's prediction of flat economic growth for the Canadian economy in 2025 suggests a period of stagnation rather than a recession. Key factors driving this forecast include global economic uncertainty, high interest rates implemented by the Bank of Canada, and, to a lesser extent, the resilience of the Canadian labor market. Understanding the implications of this forecast for consumers and businesses is crucial. To stay abreast of the evolving economic landscape and its impact, regularly consult the OECD's reports and other authoritative economic sources for updates on Canadian economic growth and its future prospects. Staying informed about the OECD forecast on Canadian economic growth is vital for informed decision-making.

Featured Posts
-
 Kyle Stowers Journaling A New Approach To Player Development Marlins
May 28, 2025
Kyle Stowers Journaling A New Approach To Player Development Marlins
May 28, 2025 -
 Acheter Le Samsung Galaxy S25 512 Go Au Prix Le Plus Bas 985 56 E
May 28, 2025
Acheter Le Samsung Galaxy S25 512 Go Au Prix Le Plus Bas 985 56 E
May 28, 2025 -
 Mc Kenna The Catalyst For Phillips Resurgence At Ipswich Town
May 28, 2025
Mc Kenna The Catalyst For Phillips Resurgence At Ipswich Town
May 28, 2025 -
 Arraez Vs Carpenter Phillies Vs Mets Who Takes The Opener
May 28, 2025
Arraez Vs Carpenter Phillies Vs Mets Who Takes The Opener
May 28, 2025 -
 Italian Open Jannik Sinners Unforgettable Encounter With Pope Leo Xiv
May 28, 2025
Italian Open Jannik Sinners Unforgettable Encounter With Pope Leo Xiv
May 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Discounted Spring Hotel Stays Up To 30 Off Lavish Hotels
May 31, 2025
Discounted Spring Hotel Stays Up To 30 Off Lavish Hotels
May 31, 2025 -
 Exploring The Boundaries Of Ai Learning Towards Responsible Ai Development And Deployment
May 31, 2025
Exploring The Boundaries Of Ai Learning Towards Responsible Ai Development And Deployment
May 31, 2025 -
 Responsible Ai Acknowledging The Limits Of Ai Learning Capabilities
May 31, 2025
Responsible Ai Acknowledging The Limits Of Ai Learning Capabilities
May 31, 2025 -
 Exploring The Boundaries Of Ai Learning A Path To Responsible Ai
May 31, 2025
Exploring The Boundaries Of Ai Learning A Path To Responsible Ai
May 31, 2025 -
 Up To 30 Off Your Luxurious Spring Hotel Awaits
May 31, 2025
Up To 30 Off Your Luxurious Spring Hotel Awaits
May 31, 2025
