Rising COVID-19 Infections: A New Variant, According To The WHO
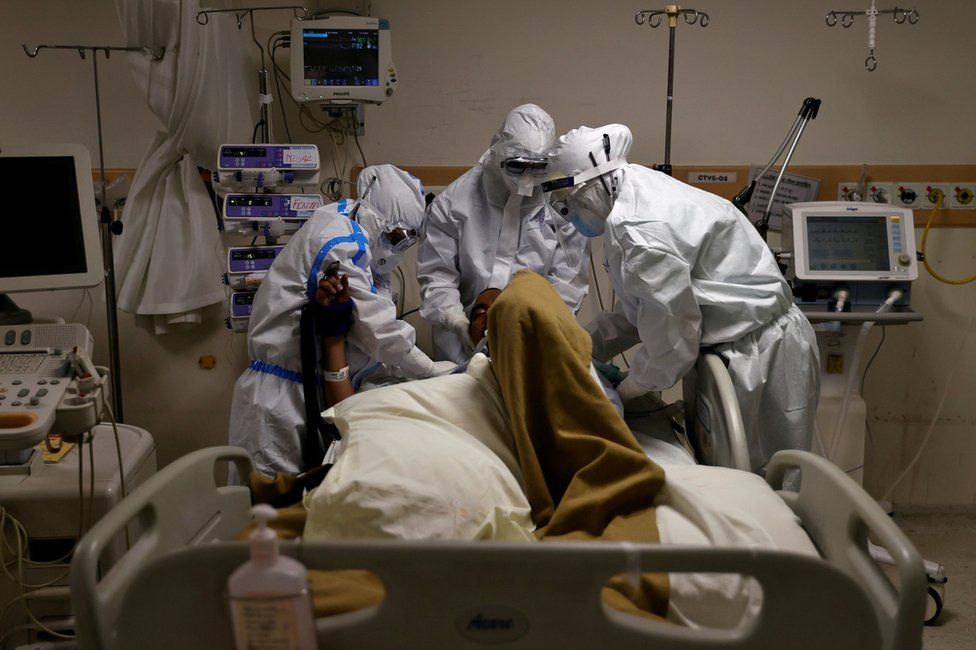
Table of Contents
A concerning surge in COVID-19 infections has been reported globally, prompting the World Health Organization (WHO) to announce the emergence of a new variant. This article delves into the details of this concerning development, examining the variant's characteristics, its spread, and the necessary precautions to mitigate its impact. We will explore the latest information and advice to help you stay informed and protected. This is a rapidly evolving situation, so please consult your local health authorities for the most up-to-date information.
Characteristics of the New COVID-19 Variant
Transmission Rate
The transmissibility of the new variant is a critical concern. While precise data is still emerging, early reports suggest a potentially higher transmission rate than previous variants like Delta and Omicron. This increased contagiousness is likely due to specific mutations impacting the virus's ability to bind to and infect human cells. The R-naught (R0) value—a measure of how many people one infected person will likely infect—is a key indicator being closely monitored. Higher R0 values indicate a greater potential for rapid community spread.
- Comparison with Previous Variants: Initial data suggests a potentially higher R0 compared to previous variants, although this requires further confirmation through ongoing research.
- Mutations and Transmissibility: Specific mutations within the viral genome are being analyzed to determine their contribution to increased transmissibility. These mutations could affect the virus's ability to evade the immune system or enhance its binding to host cells.
Severity of Symptoms
The severity of illness associated with the new variant is another crucial aspect under investigation. While early reports suggest a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, it's too early to definitively characterize its severity compared to previous variants.
- Common Symptoms: Symptoms reported so far include fever, cough, fatigue, shortness of breath, muscle aches, and loss of taste or smell. These are consistent with symptoms observed in previous variants.
- Symptom Severity and Differences: Further research is needed to determine if there are significant differences in symptom severity or the frequency of severe illness requiring hospitalization compared to earlier variants. Monitoring hospitalization rates and mortality rates is vital in assessing the variant's overall impact.
Effectiveness of Existing Vaccines and Treatments
The effectiveness of existing COVID-19 vaccines and treatments against this new variant is a major area of focus. Preliminary assessments are underway to evaluate the immune response elicited by current vaccines and the efficacy of antiviral treatments.
- Vaccine Efficacy: While the full extent of vaccine effectiveness against this new variant remains unclear, existing vaccines are still expected to provide some level of protection, particularly against severe disease. Data on reduced efficacy against infection, but continued effectiveness against serious illness, is being closely monitored.
- Updated Booster Recommendations: Health authorities may issue recommendations for updated booster shots tailored to the new variant to enhance protection as more data becomes available.
- Antiviral Treatment Effectiveness: The effectiveness of existing antiviral treatments against the new variant is also being assessed. Further research will determine if modifications to existing treatments or development of new ones is needed.
Global Spread and Impact of the New Variant
Geographic Distribution
The new variant is showing a concerning pattern of global spread, with reports of infections across numerous countries and regions. The rapid spread highlights the virus's ability to overcome geographic barriers.
- Countries and Regions Affected: Monitoring of cases is ongoing, and new outbreaks are likely to be reported as surveillance efforts continue. The initial epicenter of the outbreak remains to be definitively identified.
- Infection Hotspots: The identification of infection hotspots will allow for targeted public health interventions. This data guides resource allocation and public health messaging.
Impact on Healthcare Systems
The surge in COVID-19 infections places a significant strain on healthcare systems worldwide. Increased hospital admissions and intensive care unit (ICU) occupancy challenge the capacity of healthcare providers to effectively treat all patients.
- Healthcare Capacity: Hospitals in regions experiencing significant outbreaks are facing challenges with bed capacity, staffing shortages, and resource allocation.
- Hospital Bed Occupancy and ICU Capacity: Real-time monitoring of hospital bed occupancy and ICU capacity is critical to understanding the strain on healthcare systems and guide appropriate interventions.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Public Health Recommendations
Effective prevention and mitigation strategies remain critical to controlling the spread of the new variant. Public health measures previously implemented are still highly relevant.
- Vaccination: Vaccination remains a cornerstone of the response. High vaccination rates minimize severe illness, hospitalization, and death.
- Booster Shots: Booster shots enhance immune response and provide additional protection against infection and severe disease.
- Masking: Mask-wearing, particularly in crowded indoor settings, can help reduce transmission.
- Social Distancing: Maintaining physical distance, particularly during periods of high transmission, remains an effective preventative measure.
- Hand Hygiene: Frequent and thorough handwashing with soap and water or using an alcohol-based hand sanitizer are crucial in limiting the spread of the virus.
- Testing: Regular testing, particularly for those with symptoms or exposure, aids in early identification and isolation of infected individuals.
Individual Protective Measures
Individuals can take several steps to protect themselves and others from infection.
- Mask Usage: Choose well-fitting masks (N95 or KN95 recommended) when in crowded indoor spaces or around vulnerable individuals.
- Handwashing: Wash your hands frequently and thoroughly, especially after touching surfaces in public areas.
- Social Distancing: Maintain a safe distance from others, particularly in crowded settings.
- Avoiding Crowded Spaces: Limit exposure to crowded indoor environments, as these are high-risk areas for transmission.
Conclusion
The emergence of a new COVID-19 variant, as reported by the WHO, highlights the ongoing need for vigilance and proactive measures to control the pandemic. Understanding the variant's characteristics, its global spread, and effective prevention strategies are crucial for mitigating its impact. Staying informed about the latest developments, following public health recommendations, and practicing individual protective measures are vital steps in protecting yourself and your community from rising COVID-19 infections caused by this new variant. Continue to monitor updates from the WHO and your local health authorities regarding this evolving situation and the ongoing threat of new COVID-19 variants. Take proactive steps to protect yourself and your community from the threat of rising COVID-19 infections.

Featured Posts
-
 Munguias Revenge Dominant Victory Over Surace In Rematch
May 31, 2025
Munguias Revenge Dominant Victory Over Surace In Rematch
May 31, 2025 -
 Retrait Du Trait De Cote A Saint Jean De Luz Une Necessaire Derogation Pour La Preservation Du Littoral
May 31, 2025
Retrait Du Trait De Cote A Saint Jean De Luz Une Necessaire Derogation Pour La Preservation Du Littoral
May 31, 2025 -
 La Mejor Receta De Lasana De Calabacin Facil Estilo Pablo Ojeda Mas Vale Tarde
May 31, 2025
La Mejor Receta De Lasana De Calabacin Facil Estilo Pablo Ojeda Mas Vale Tarde
May 31, 2025 -
 Canadian Job Market Update Rosenbergs Analysis And Implications For Interest Rates
May 31, 2025
Canadian Job Market Update Rosenbergs Analysis And Implications For Interest Rates
May 31, 2025 -
 Skywarn Spotter Training Spring Session Tom Atkins
May 31, 2025
Skywarn Spotter Training Spring Session Tom Atkins
May 31, 2025
