Trump Administration's Response To Harvard Lawsuit: Open To Negotiation?

Table of Contents
The Harvard Lawsuit: A Recap of the Affirmative Action Debate
The Students for Fair Admissions (SFFA) lawsuit against Harvard University centers on the allegation that the university's admissions process discriminates against Asian-American applicants. SFFA argues that Harvard's consideration of race as a factor in admissions violates Title VI of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, which prohibits discrimination based on race, color, or national origin in programs receiving federal funding. This case reignited the long-standing national debate surrounding affirmative action – the practice of considering race as one factor among many in college admissions to promote diversity.
- Key arguments presented by SFFA: Statistical disparities in admission rates between Asian-American applicants and other racial groups; allegations of subjective scoring and bias in application reviews; the claim that race-neutral alternatives would achieve similar levels of diversity.
- Harvard's defense strategy: Emphasis on the educational benefits of diversity; arguments that race is considered holistically and not as a decisive factor; the assertion that a race-blind admissions process would harm diversity and violate the university's educational mission.
- Previous legal challenges to affirmative action: The Supreme Court has addressed affirmative action in higher education in several cases, including Grutter v. Bollinger (2003) and Fisher v. University of Texas (2013), establishing a framework for permissible consideration of race in admissions while prohibiting quotas or separate tracks for different racial groups. The Harvard case represents a significant new challenge to this established legal framework.
The Trump Administration's Initial Response: A Firm Stance Against Affirmative Action?
The Trump administration, through the Department of Justice (DOJ), initially appeared to take a firm stance against Harvard's affirmative action policies. The DOJ filed an amicus brief supporting SFFA, arguing that Harvard's admissions process violated the Civil Rights Act. This intervention significantly escalated the stakes of the lawsuit, lending the weight of the federal government to the arguments against affirmative action.
- Specific statements made by administration officials: Public statements from officials emphasized the administration's commitment to merit-based admissions and opposition to race-based preferences.
- Actions taken by the Department of Justice or other agencies: Filing of amicus briefs in support of SFFA; potential investigations into other universities with similar admissions policies (though these actions were less consistently reported across different administrations).
- Public perception of the administration's position: The administration's stance was widely seen as aligning with a conservative perspective on affirmative action, fueling existing political divisions surrounding the issue.
Signs of Potential Negotiation: Analyzing Shifting Rhetoric and Actions
While the Trump administration's initial response seemed uncompromising, subtle shifts in rhetoric and actions might suggest a potential openness to negotiation. While direct evidence of formal negotiations remains scarce, the absence of overt escalation and the ongoing legal process could be interpreted as indicating a willingness to explore alternative resolutions.
- Examples of potentially conciliatory statements: (Note: This section would require detailed research to identify specific instances of potentially conciliatory language from administration officials. Absence of such instances would weaken this argument.) Absence of inflammatory statements following key court rulings could be interpreted as a sign of cautiousness.
- Evidence of back-channel communications: (This section would require investigative journalism to uncover any behind-the-scenes communications. The lack of public information would necessitate speculation and caution.)
- Possible motivations for seeking a negotiated settlement: Avoiding a Supreme Court ruling that could set a sweeping precedent; minimizing potential political backlash; preserving resources that could be allocated to other legal priorities.
The Potential Benefits and Drawbacks of a Negotiated Settlement
A negotiated settlement could offer mutual benefits. Harvard might avoid a potentially unfavorable Supreme Court ruling that could fundamentally alter its admissions process. SFFA could secure concessions regarding the role of race in admissions, even if short of a complete ban.
- Benefits for Harvard: Avoiding a costly and lengthy legal battle; preserving its reputation; maintaining some flexibility in its admissions process.
- Benefits for SFFA: Securing at least some policy changes at Harvard; setting a precedent that could influence other universities; achieving some of their stated goals even without a full legal victory.
- Potential drawbacks for both parties: A settlement might be perceived as a compromise that satisfies neither side fully; the terms of any settlement could be subject to public scrutiny and criticism.
Conclusion
The Trump administration's response to the Harvard lawsuit, initially characterized by a firm stance against affirmative action, presented a complex picture regarding the potential for negotiation. While direct evidence of negotiations remains elusive, the absence of overt hostility and the protracted legal process leave open the possibility of a negotiated settlement. The Supreme Court's eventual decision, regardless of whether a settlement is reached, will have profound implications for affirmative action in higher education. Stay informed on the developments in the Trump Administration's response to the Harvard lawsuit and the ongoing debate surrounding affirmative action in college admissions. Continue to follow this critical legal battle as it unfolds and shapes the future of higher education.

Featured Posts
-
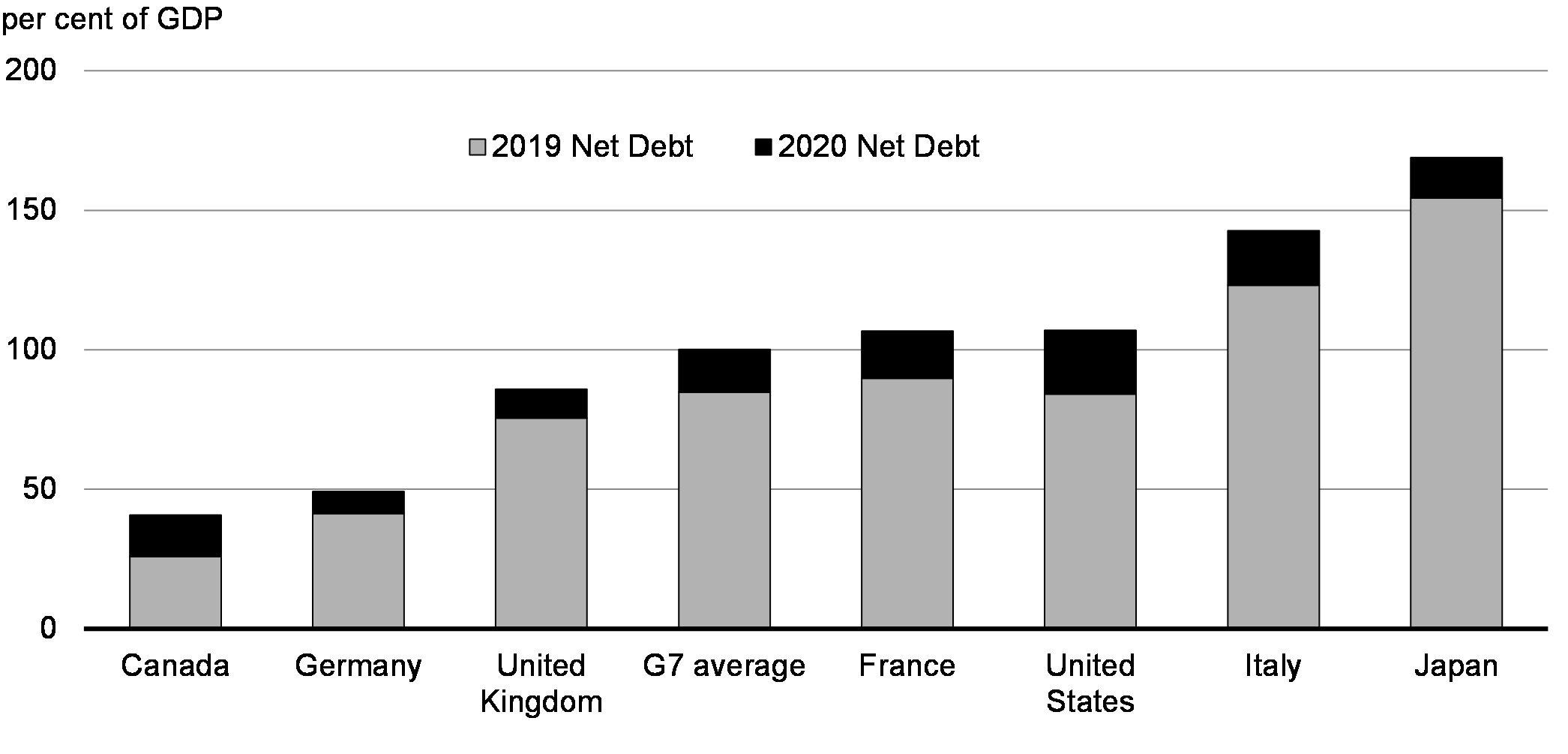 Is Canadas Fiscal Policy Sustainable Examining Liberal Economic Policies
Apr 24, 2025
Is Canadas Fiscal Policy Sustainable Examining Liberal Economic Policies
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Trumps Immigration Enforcement New Legal Obstacles Emerge
Apr 24, 2025
Trumps Immigration Enforcement New Legal Obstacles Emerge
Apr 24, 2025 -
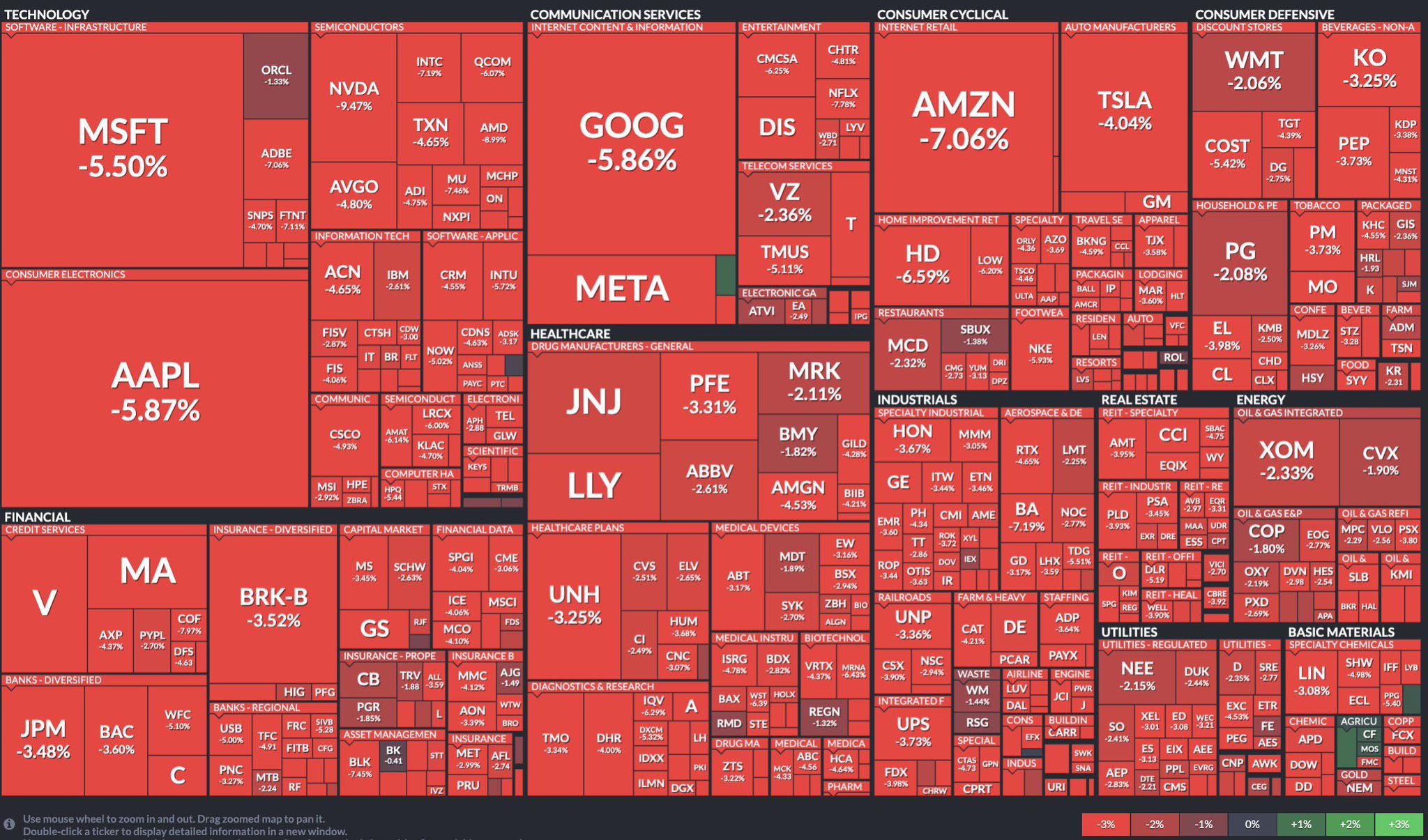 Stock Market Today Dow S And P 500 Live Updates For April 23rd
Apr 24, 2025
Stock Market Today Dow S And P 500 Live Updates For April 23rd
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Car Dealers Renew Opposition To Ev Mandates Industry Fights Back
Apr 24, 2025
Car Dealers Renew Opposition To Ev Mandates Industry Fights Back
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Houston Isd Mariachis Road To Uil State A Viral Whataburger Success Story
Apr 24, 2025
Houston Isd Mariachis Road To Uil State A Viral Whataburger Success Story
Apr 24, 2025
