Will Anyone Fill Trump's Promised Restored American Factory Jobs?

Table of Contents
Assessing the Reality: Manufacturing Job Growth Under Trump and Beyond
Job Numbers: A Statistical Analysis
During Trump's presidency (2017-2021), the US manufacturing sector did see some job growth. However, the numbers fell significantly short of the dramatic increases promised.
- Official BLS Data: The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reported a net gain of approximately [Insert actual BLS data here] manufacturing jobs during this period. This represents a [calculate percentage increase/decrease] change compared to the pre-Trump era.
- Sectoral Shifts: While some sectors experienced growth (e.g., [cite specific examples from BLS data, such as food processing or specialized machinery]), others continued to decline (e.g., [cite specific examples, such as textiles or apparel]). This uneven growth highlights the complexities of the issue.
The Role of Automation: A Technological Tide
Automation and technological advancements have profoundly impacted manufacturing employment. The rise of robots, AI, and advanced manufacturing technologies has significantly reduced the need for manual labor.
- Job Displacement: Automation has led to job losses in areas such as assembly line work, basic machining, and repetitive tasks.
- New Skill Requirements: While some jobs have been lost, automation has also created new roles requiring specialized skills in areas like robotics programming, data analysis, and maintenance of automated systems.
- Retraining Initiatives: Addressing the skills gap created by automation requires significant investment in retraining programs to equip workers with the skills needed for these new roles. Government initiatives and private sector partnerships are crucial for successful retraining.
Factors Hindering Job Reshoring: Why Factories Aren't Returning in Droves
Global Competition: A Level Playing Field?
The US faces stiff competition from countries with lower labor costs and manufacturing expenses. This global competition significantly impacts the decision of companies to bring manufacturing back to the US.
- Global Supply Chains: Established global supply chains often make it more cost-effective for companies to continue manufacturing overseas.
- Competitiveness: Countries like China and Vietnam offer significantly lower labor costs and often have more relaxed environmental regulations, making them attractive destinations for manufacturing.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Restructuring: Navigating Uncertainty
Recent global events, including the COVID-19 pandemic, have exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains, prompting companies to rethink their strategies.
- Nearshoring and Regionalization: Many companies are exploring "nearshoring," shifting production to countries closer to their markets to reduce reliance on distant supply chains. This trend could potentially benefit North American manufacturing.
- Strategic Adaptation: Businesses are adopting more resilient strategies to mitigate risks associated with global instability, including diversification of suppliers and increased inventory levels.
The Skills Gap: A Mismatch of Skills and Needs
A significant skills gap exists between the available workforce and the demands of modern manufacturing. This mismatch hinders the creation of new jobs.
- Demand for Skilled Workers: Modern manufacturing requires workers with advanced skills in areas such as robotics, advanced materials science, and data analytics.
- Bridging the Gap: Addressing this skills gap necessitates significant investment in vocational training, apprenticeships, and educational programs that align with industry needs. Collaboration between educational institutions and businesses is critical.
Potential Pathways to Growth: Strategies for Creating American Manufacturing Jobs
Investment in Infrastructure and Technology: Laying the Foundation
Government investment in infrastructure (transportation networks, energy grids) and advanced manufacturing technologies is vital for boosting competitiveness.
- Incentives and Tax Breaks: Tax incentives and other government support for businesses investing in advanced manufacturing can encourage domestic production.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between the public and private sectors can leverage resources and expertise to drive innovation and job creation.
Promoting Reshoring and Nearshoring: Bringing Jobs Home
Policies and strategies designed to incentivize companies to bring manufacturing back to the US or nearby countries are crucial.
- Trade Agreements and Tariffs: Strategic use of trade agreements and tariffs can level the playing field for American manufacturers.
- Successful Reshoring Examples: Studying successful reshoring initiatives can offer valuable lessons and best practices.
Investing in Workforce Development: Cultivating Talent
Investing in training and education is essential to equip workers with the skills needed for modern manufacturing jobs.
- Apprenticeships and Vocational Training: Expanding apprenticeship programs and vocational training initiatives can provide a pipeline of skilled workers.
- Industry-Education Collaboration: Strong partnerships between educational institutions and businesses ensure that training programs align with industry needs.
The Future of American Manufacturing Jobs: A Look Ahead
The resurgence of American manufacturing jobs faces significant challenges, including global competition, automation, and the skills gap. While some job growth occurred under the Trump administration, the ambitious goals of completely reversing decades of job losses remain difficult to achieve. The path forward requires a multi-faceted approach involving government investment in infrastructure and technology, strategic trade policies to promote reshoring and nearshoring, and a commitment to robust workforce development initiatives. Will we truly see the promised restored American factory jobs? The answer depends on the concerted effort of government, industry, and educational institutions to address these complex challenges. Share your thoughts on how we can create more American manufacturing jobs in the comments below!

Featured Posts
-
 Full Solutions Nyt Mini Crossword For March 24 2025
May 21, 2025
Full Solutions Nyt Mini Crossword For March 24 2025
May 21, 2025 -
 Ten Man Juventus Held To 1 1 Draw By Lazio In Serie A Thriller
May 21, 2025
Ten Man Juventus Held To 1 1 Draw By Lazio In Serie A Thriller
May 21, 2025 -
 Tikkie En Nederlandse Bankrekeningen Een Complete Gids
May 21, 2025
Tikkie En Nederlandse Bankrekeningen Een Complete Gids
May 21, 2025 -
 Record 19 Indian Paddlers Compete In Wtt Star Contender Chennai
May 21, 2025
Record 19 Indian Paddlers Compete In Wtt Star Contender Chennai
May 21, 2025 -
 Kanali Mi Ukrayina 5 Kanal 1 1 Pryamiy Inter Ictv Noviy Kanal Stb Up Ta Nv Ofitsiyne Pidtverdzhennya Statusu
May 21, 2025
Kanali Mi Ukrayina 5 Kanal 1 1 Pryamiy Inter Ictv Noviy Kanal Stb Up Ta Nv Ofitsiyne Pidtverdzhennya Statusu
May 21, 2025
Latest Posts
-
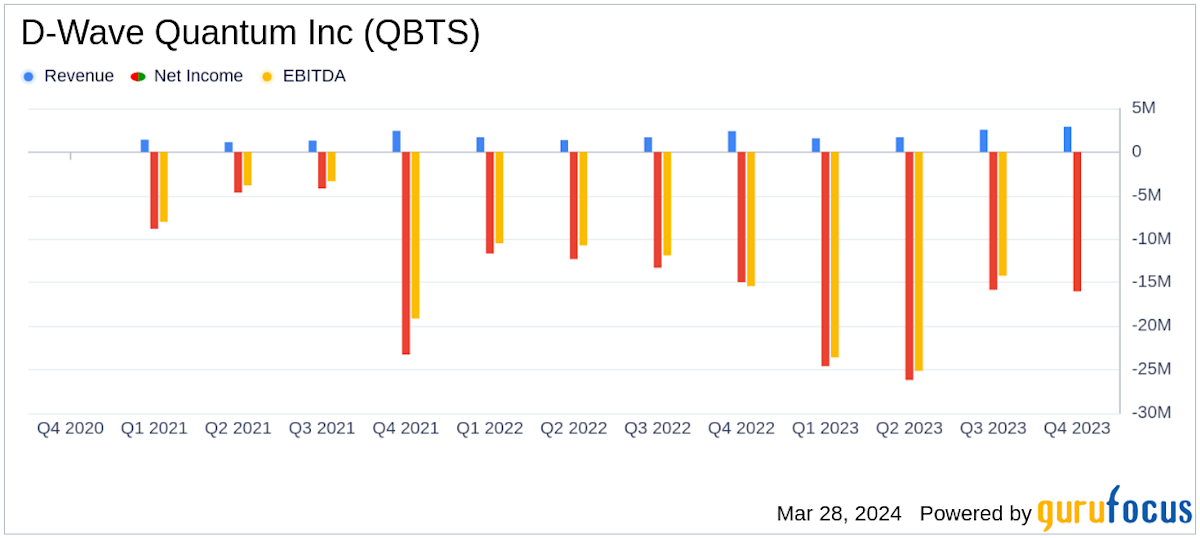 Factors Contributing To D Wave Quantum Qbts Stocks Friday Gains
May 21, 2025
Factors Contributing To D Wave Quantum Qbts Stocks Friday Gains
May 21, 2025 -
 Bbai Stock Exploring The Potential For Growth And Challenges
May 21, 2025
Bbai Stock Exploring The Potential For Growth And Challenges
May 21, 2025 -
 Analyzing The Friday Increase In D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Value
May 21, 2025
Analyzing The Friday Increase In D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Value
May 21, 2025 -
 Big Bear Ai Bbai Stock Upgrade Defense Sector Investment Opportunities
May 21, 2025
Big Bear Ai Bbai Stock Upgrade Defense Sector Investment Opportunities
May 21, 2025 -
 Will Big Bear Ai Bbai Stock Skyrocket A Realistic Look At Its Future
May 21, 2025
Will Big Bear Ai Bbai Stock Skyrocket A Realistic Look At Its Future
May 21, 2025
