Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF: How To Interpret Its Net Asset Value
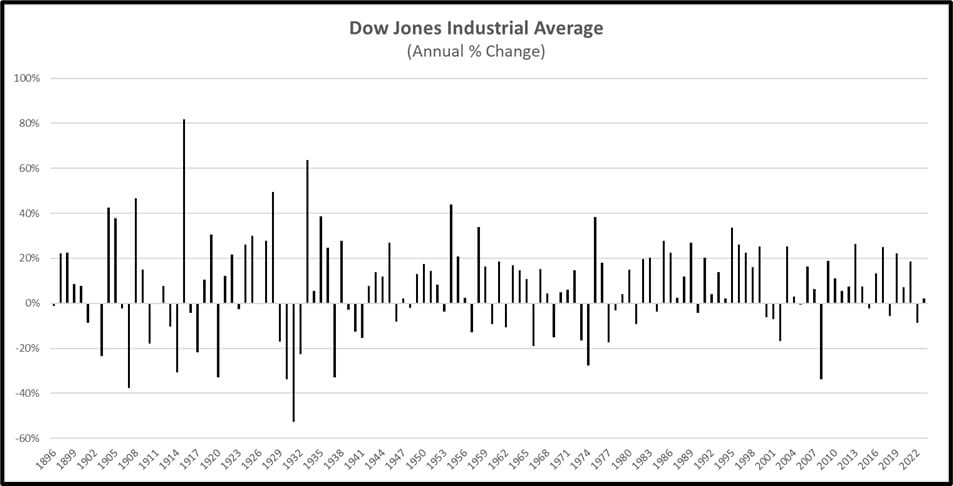
Table of Contents
Understanding Net Asset Value (NAV) in ETFs
Net Asset Value (NAV) represents the net value of an ETF's assets minus its liabilities, divided by the number of outstanding shares. Essentially, it's the per-share value of the ETF's holdings. For the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF, the NAV reflects the collective value of its holdings in the 30 companies that make up the Dow Jones Industrial Average.
How NAV is Calculated for the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF:
The calculation involves several steps:
- Market value of underlying assets: This is determined by multiplying the current market price of each of the 30 Dow Jones Industrial Average component stocks by the number of shares the ETF holds in each.
- Less: ETF expenses and fees: This includes management fees, administrative costs, and other expenses incurred by the ETF provider.
- Divided by: Number of outstanding shares: The total net asset value is then divided by the total number of Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF shares outstanding to arrive at the NAV per share.
Daily NAV Updates and Availability:
The NAV of the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF is typically calculated and published daily, usually at the close of the market. You can find this information on the Amundi website, major financial news websites, and through your brokerage account.
NAV vs. Market Price:
While the NAV represents the intrinsic value of the ETF, the market price is the actual price at which the ETF is trading on the exchange. These values might differ due to supply and demand factors. A higher market price than NAV suggests high demand, and vice-versa.
Interpreting the NAV of the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF for Investment Decisions
Understanding and interpreting the NAV is vital for informed investment choices.
Monitoring NAV Trends:
Tracking the NAV over time allows you to assess the ETF's performance. Consistent upward trends indicate positive growth, while downward trends signal potential losses. Analyzing longer-term trends provides a clearer picture of the ETF's performance than short-term fluctuations.
Comparing NAV to Benchmark:
Comparing the Amundi DJIA UCITS ETF NAV to the actual Dow Jones Industrial Average index value helps assess the ETF's performance relative to its benchmark. Small discrepancies are normal due to expenses and tracking differences. Significant deviations require closer scrutiny.
Using NAV for Buy/Sell Decisions:
While NAV is a crucial factor, it shouldn't be the sole determinant of buy/sell decisions. Consider other factors like market trends, your investment goals, and risk tolerance. A low NAV might present a buying opportunity, but a thorough market analysis is always recommended.
NAV and Risk Assessment:
High NAV fluctuations indicate higher risk. Investors with lower risk tolerance might prefer ETFs with more stable NAVs, potentially sacrificing some potential returns.
Factors Affecting the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF NAV
Several factors influence the NAV of the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF.
Market Fluctuations:
Changes in the market value of the Dow Jones Industrial Average's component stocks directly impact the ETF's NAV. A strong market generally leads to a higher NAV, while a downturn reduces it.
Currency Exchange Rates:
If the ETF is denominated in a currency different from your base currency, exchange rate fluctuations can influence the NAV you see in your account.
Dividend Distributions:
When underlying companies pay dividends, the ETF receives these payments, which can positively impact the NAV (though the immediate impact might be offset by the distribution itself).
Management Fees:
Management fees and other expenses reduce the NAV over time. These fees are deducted from the overall asset value, impacting the NAV per share.
Conclusion: Mastering the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF NAV
Understanding the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF NAV is essential for making well-informed investment decisions. By monitoring NAV trends, comparing it to the benchmark index, and considering other market factors, you can better assess the performance and risk associated with this ETF. Remember to utilize the NAV alongside other analytical tools and consider your individual investment strategy. To learn more about the Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average UCITS ETF and access its current NAV, visit the Amundi website [link to Amundi website]. Mastering the Amundi DJIA UCITS ETF NAV empowers you to make smarter investment choices. Understanding the Dow Jones Industrial Average ETF NAV interpretation is critical for successful ETF investing.

Featured Posts
-
 Glastonbury 2024 Unannounced Us Band Teases Festival Appearance
May 24, 2025
Glastonbury 2024 Unannounced Us Band Teases Festival Appearance
May 24, 2025 -
 Sergey Yurskiy 90 Let Geniyu Paradoksov
May 24, 2025
Sergey Yurskiy 90 Let Geniyu Paradoksov
May 24, 2025 -
 Da Nike A Lululemon Analisi Dell Impatto Dei Dazi Trump Del 20
May 24, 2025
Da Nike A Lululemon Analisi Dell Impatto Dei Dazi Trump Del 20
May 24, 2025 -
 Analiz Svadebnykh Tseremoniy Na Kharkovschine 600 Brakov V Mesyats
May 24, 2025
Analiz Svadebnykh Tseremoniy Na Kharkovschine 600 Brakov V Mesyats
May 24, 2025 -
 Bangladesh Businesses In Europe A Collaborative Path To Success
May 24, 2025
Bangladesh Businesses In Europe A Collaborative Path To Success
May 24, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Apple Stock And Tariffs Assessing The Risks To Buffetts Portfolio
May 24, 2025
Apple Stock And Tariffs Assessing The Risks To Buffetts Portfolio
May 24, 2025 -
 Analysts 254 Apple Stock Prediction Time To Buy
May 24, 2025
Analysts 254 Apple Stock Prediction Time To Buy
May 24, 2025 -
 Buffetts Apple Investment Navigating The Impact Of Trump Era Tariffs
May 24, 2025
Buffetts Apple Investment Navigating The Impact Of Trump Era Tariffs
May 24, 2025 -
 Apple Stock 200 Entry Point Before 254 Target
May 24, 2025
Apple Stock 200 Entry Point Before 254 Target
May 24, 2025 -
 Apple Vs Trump Tariffs Will Buffetts Top Tech Stock Crack
May 24, 2025
Apple Vs Trump Tariffs Will Buffetts Top Tech Stock Crack
May 24, 2025
